The pandemic has accelerated digital transformation across the world. But, behind the scenes, telcos are still facing a significant tech debt, and many are committed to continuing the innovation.
That’s for good reason. Today’s digital customers increasingly expect a digital-first customer experience in telecom. The days of visiting a local store to purchase or manage telecoms products and services are fading away. Digital-first telcos have risen to the occasion, transforming the market and meeting the growing digital demand. For traditional telcos, waiting to innovate is no longer an option—it’s a must to remain competitive.
So what comes next? Here are the technology trends in telecom industry that stand to impact and transform telecoms services in the future.
RECOMMENDED READING
The rapid rise of low-code/no-code solutions
What are low-code/no-code solutions?
Historically, telecom companies had only two options when they needed new technology solutions. The first option was to build a new system in-house. This approach tends to be more tailored to the service provider’s needs and business requirements. However, it typically means more in-house resources, higher costs and a longer deployment time. Alternatively, a provider could buy a system from an external vendor. This approach is usually less effort from the service provider and much cheaper. Systems are installed much faster but they are not custom-fit. Therefore, the service provider loses some flexibility in making future changes.
More recently, however, a third alternative emerged and it is now one of the top tech trends in telecom industry. Low code/no code (LC/NC) solutions are designed to make it relatively easy for companies to design, build and launch applications quickly and hassle-free. According to a recent survey from TechRepublic, nearly half of companies already use LC/NC platforms. The same report notes that among companies not using LC/NC solutions, one in five plans to begin within the year.
Why are low-code/no-code solutions becoming more popular?
The driving force behind this trend is the global shortage of digital skills, from software development to data analytics to information security. The pool of technical talent has long been smaller than the demand, and the Great Resignation has only exacerbated the problem.
Amidst this ongoing talent shortage, there’s another stressor—the need to deploy technology products to market faster and faster. LC/NC solutions answer these challenges by making doing so easier and quicker. The technology democratizes software development, allowing business users—or citizen developers—in different functions to design and deploy applications.
With the skills gap likely to continue, the interest in LC/NC solutions will too. LC/NC solutions can enable telcos to keep pace with technology changes and meet the digital demand, even with limited technical resources. However, as with many automation tools, efficiency in development activities often come at the expense of customisability.
It is argued that the best time to use LC/NC is when the organisation needs to build software that is not unique or does not drive significant business value.
We ran a short LinkedIn poll recently. It returned some interesting results about what service providers prefer for their software development approach when it comes to Digital:

Link to the LinkedIn post: HERE
Leveraging data will require adding value—and engendering trust
Gone are the days when data analytics was considered a secondary or additional activity. Companies across all industries are embracing data analytics as a key business driver for smart decision-making and increased personalisation of user experience.
Telcos have, in varying degrees, used advanced data analytics to provide consumers with more personalised products. And consumers have been on board as long as they see the benefit. In fact, a survey performed by Merkle in 2021 showed that 76% of the respondents would fill a short survey when they visit a website for the first time to get a more personalised experience, compared to 71% the year before. This implies that customers are becoming more comfortable sharing their data with businesses for better experiences.
However, this research speaks to growing tension between consumers and service providers. The first want more personalised services, but they are also more selective about which companies they share data with. A recent McKinsey study revealed that some 44 per cent of digital consumers say that they don’t fully trust digital services.
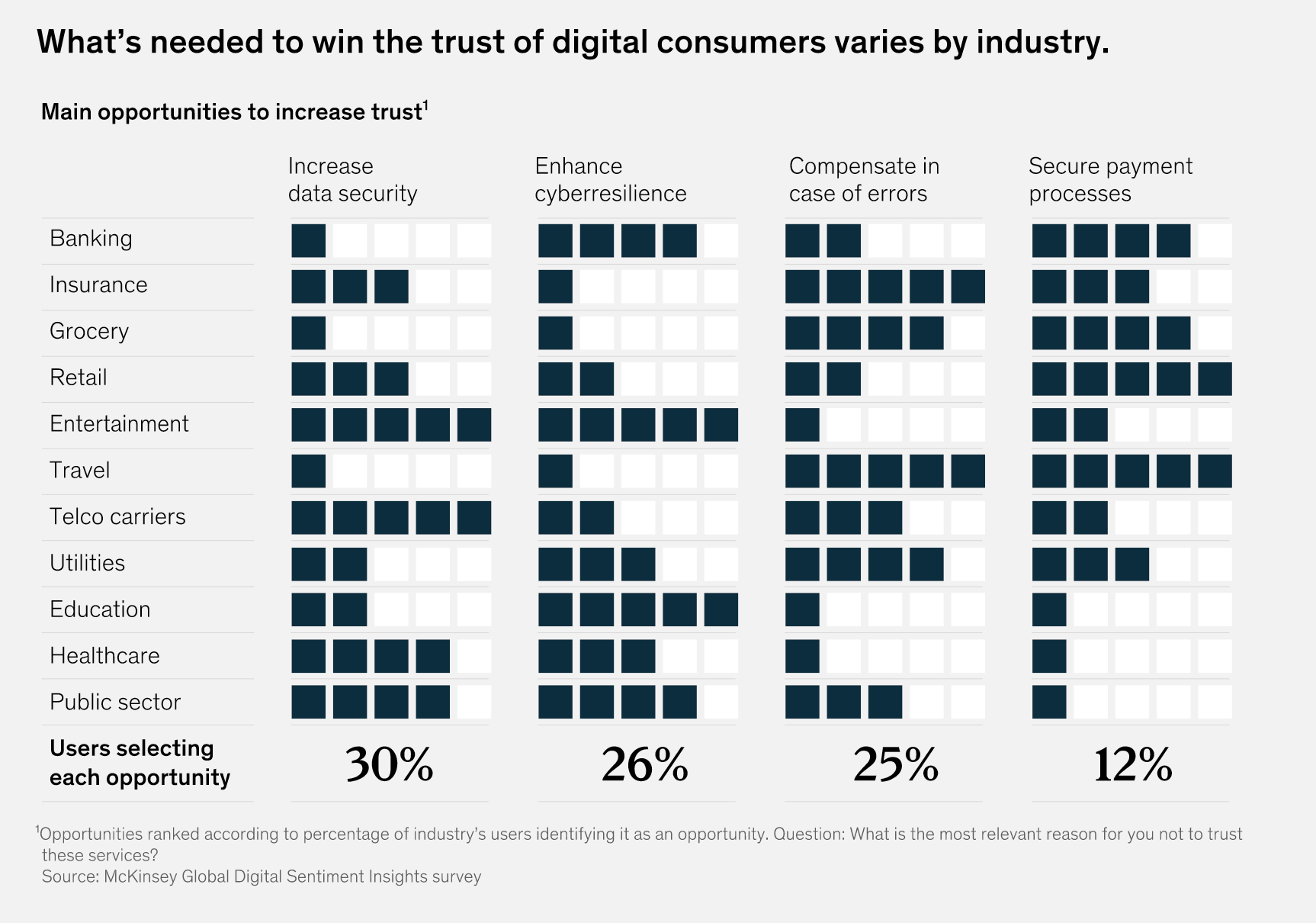
This presents another one of the tech trends in telecom industry. Organisations that want to build and keep consumer trust will need to be thoughtful about the data they ask for. They will also need to be increasingly transparent about how they plan to use it.
Doubling down on AI but looking for ROI in the process
AI has proven helpful in multiple ways, from powering recommendation engines and chatbots within the retail world to improving fraud analysis and prevention in the banking industry. But there’s still so much more organisations can do, especially with the AI they already have.

Telcos have invested significant resources into AI solutions, such as Vodafone with their AI chatbot TOBi. TOBi uses artificial intelligence that understands customers in context. Subsequently, it provides fast, consistent and accurate answers across any application, device, or channel. It’s also a central component of Vodafone’s strategy to digitally transform their operations and deliver operating cost efficiencies. In their H1 2021 results, Vodafone reported 29m AI conversations per month in 16 countries.
However, only 20% of AI models are ever used in widespread deployment. What’s more, the current average return on AI investments hovers around 1%. AI is not easy to deliver. There is a fine line between saving customers time and creating frustration with unhelpful or inconsistent responses.
This year, expect to see more organisations examining the ROI of AI-powered technology and looking to get more from the investments they’ve made. Automation Technology partners can help by identifying additional opportunities for AI models to drive customer engagement, validate credit scoring, and protect businesses against fraud.
Open APIs and eSIM-as-a-Service will yield even more choices—and more competition
There have long been high barriers that protect traditional telecom service providers from new competition. But the advent of open APIs and the eSIM-as-a-Service model is knocking them down, creating yet another trend in telecoms industry. It yields a considerable influx of new business models that provide connectivity-like services. Open APIs programs, such as those championed by TM Forum, will drive more integrated telco and non-telco products and services portfolios allowing service providers to leverage their customer relationships to drive incremental revenue.
In my recent post, I discussed the ambition of 5G operators and their partners to generate income from value-added services through partnerships, which has risen noticeably from a couple of years ago. In 2019, when the first commercial 5G services were only half a year old, nearly half of the survey respondents believed that telecom operators’ revenue coming from services provided through 3rd-party partnerships wouldn’t surpass 10%. Now, two years later, 55% of the respondents believe such services will generate between 10% and 30% of 5G operators’ total revenues by 2025. A further 23% see this number as going above 30%.
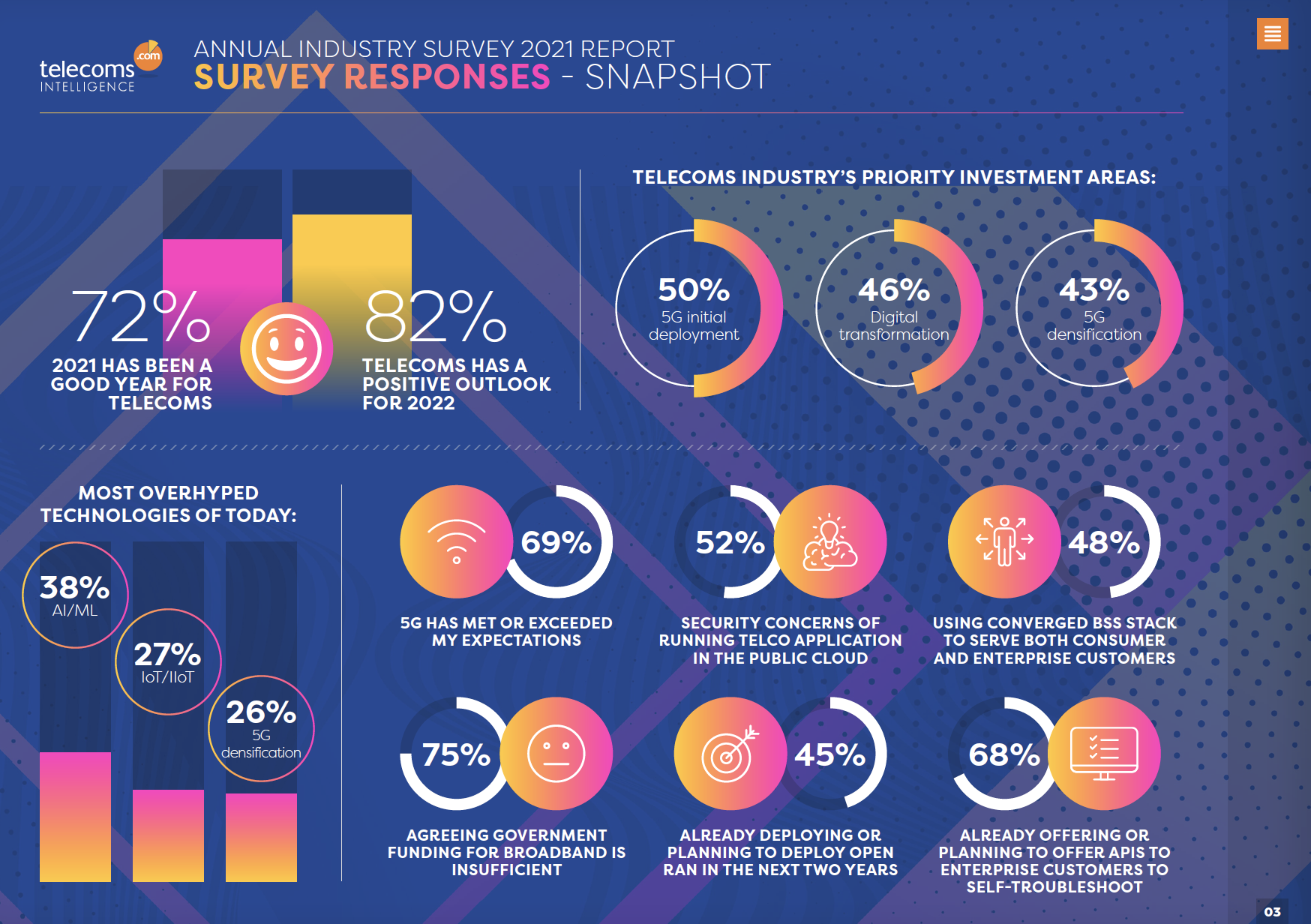
I suggest this rise in ambition to drive 3rd party revenue opportunities ties into the realisation that 5G is not delivering the amount of revenue uplift that telcos had hoped for. Therefore, telcos are searching for new revenue streams to pay for 5G investments. Additionally, I believe there is a growing appreciation that the customer relationship is the most important asset telcos have, as opposed to the network. And by fostering trust in that relationship telcos earn themselves the ability to leverage those relationships into new sales opportunities.
However, a lot of pieces need to align for telcos to achieve this not least of which is technical agility and all the business process that allows that.
RECOMMENDED READING
Conclusion
These trends in telecom are reshaping the telecom IT and BSS landscape. In the process, they’re bringing new solutions to consumers and new opportunities to traditional and non-traditional service providers alike. Brands that keep pace with these tech trends in telecom industry will lay the foundation for their next generation of customers as well as the future of their business.