What is eUICC? Is there any difference between eUICC vs eSIM? Or are they the same thing?
eSIM comes with many underlying components and definitions. It’s what makes it hard to understand.
In this blog, we’ll go over the basics of eSIM and eUICC and find out the differences between them.
TL;DR
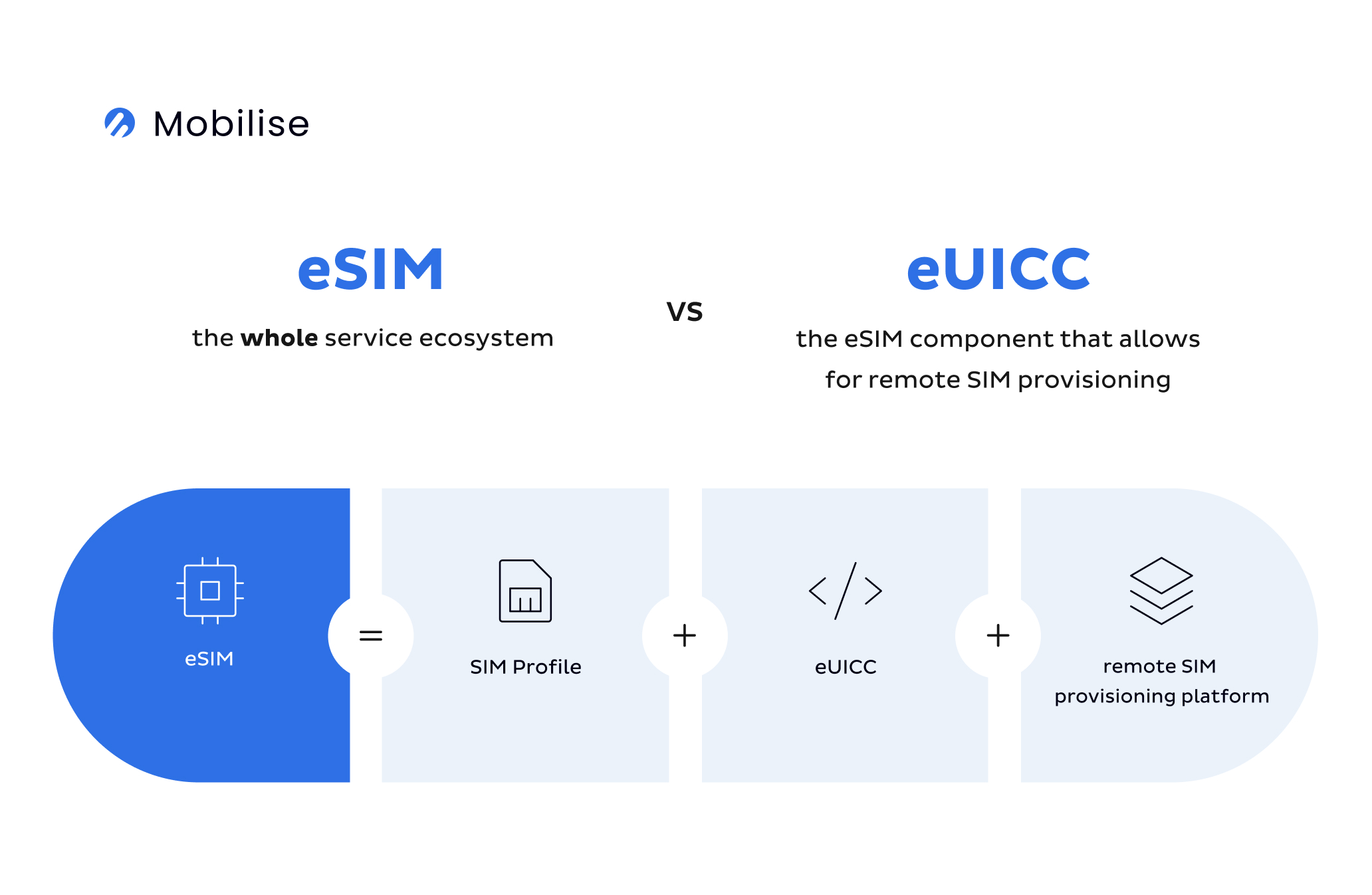
- eSIM is a digital alternative to a plastic SIM card. The term ‘eSIM’ refers to the whole eSIM ecosystem – the eSIM chip, the eSIM profile, and the remote SIM provisioning platform.
- eUICC also referred to as an eSIM chip, is a hardware component that holds operator profiles and allows for remote SIM provisioning.
- The main difference between eSIM and eUICC is that eUICC is a part of eSIM and not the full eSIM ecosystem.
What is eSIM?
In layman’s terms, an eSIM is a digital, non-removable SIM card.
Traditional physical SIM cards store the authentication parameters – international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its key (Ki) – needed to connect a device to a network provider.
eSIM serves the same purpose. But instead of being a plastic card it’s physically integrated into the device — i.e., it can’t be removed from the device and replaced with another SIM.
Additionally, eSIMs don’t have authentication parameters pre-programmed on them. The parameters are stored on an eSIM profile instead, which the user must download over the air and activate via a remote SIM provisioning (RSP) process.
Even though the process may seem more complicated, it only takes a minute. The upside, however, is significant. Whereas a plastic SIM card is pre-programmed and only allows a user to connect to one network provider, eSIM is reprogrammable and can hold multiple eSIM profiles at once. The user chooses which one to use and can seamlessly switch between them with as little as a tap of their finger.
RECOMMENDED READING
How eSIM works
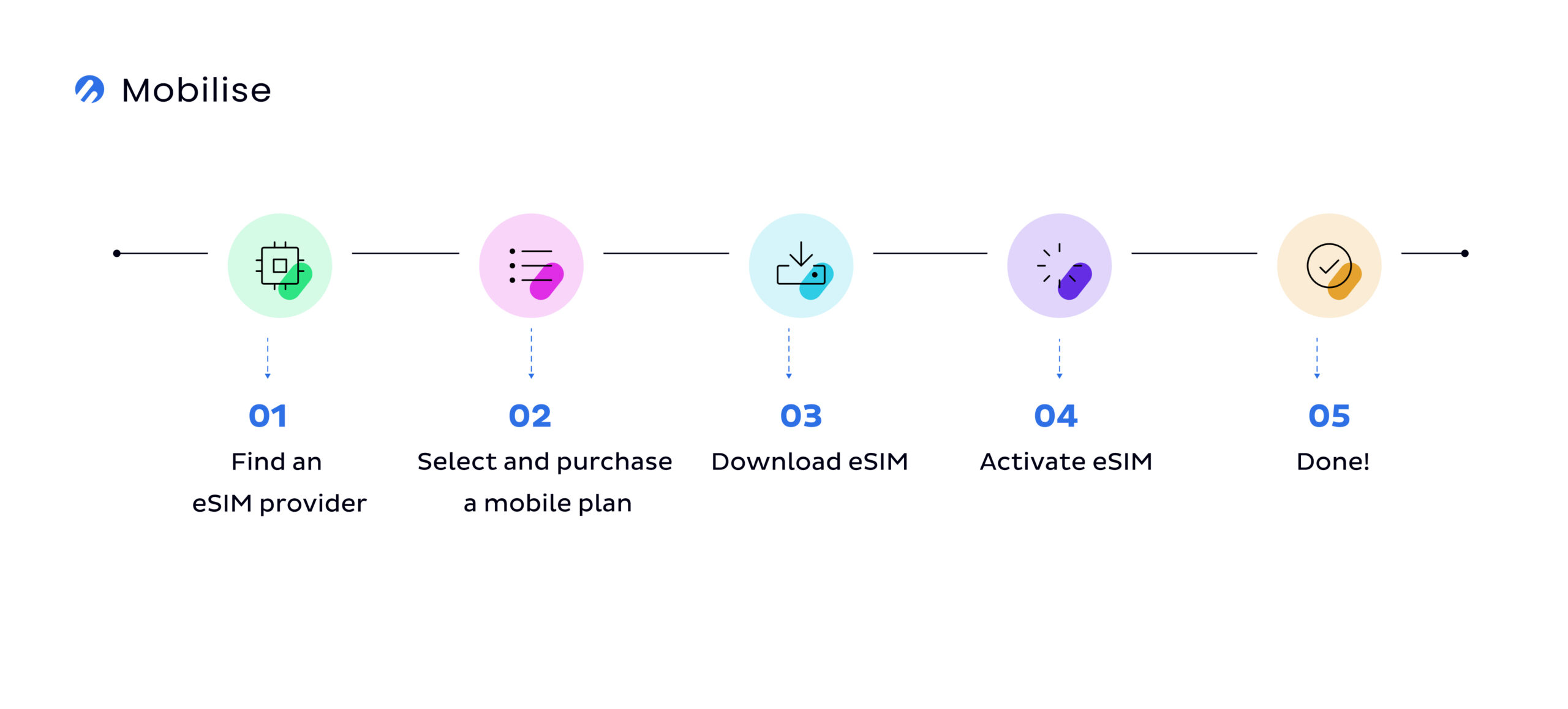
To make eSIM work, a user needs to follow a few simple steps:
- Find an eSIM provider – this step is the same for traditional SIM and eSIM users. They must find a provider that suits their needs be it price, coverage or simply a personal preference.
- Select and purchase a mobile plan – Once the user finds a suitable mobile network provider, they must select a plan that they’ll then use to connect with other people and/or the internet.
- Download your eSIM profile – here’s where things get a little different. Whereas a traditional SIM user must now purchase their plastic SIM card, the eSIM user has to download the eSIM profile from their provider onto their device. The eSIM profile contains the authentication parameters necessary to activate the eSIM.
- Activate eSIM – once the eSIM profile is on the user’s device, it has to be activated to connect the user to their chosen network provider. The most common way to do so is either through a QR code or in-app eSIM provisioning.
- Done – when the eSIM is activated, the user has access to their network provider and can perform actions covered by the mobile plan they purchased.
What is eUICC
To understand what is eUICC, we first need to define UICC, its predecessor.
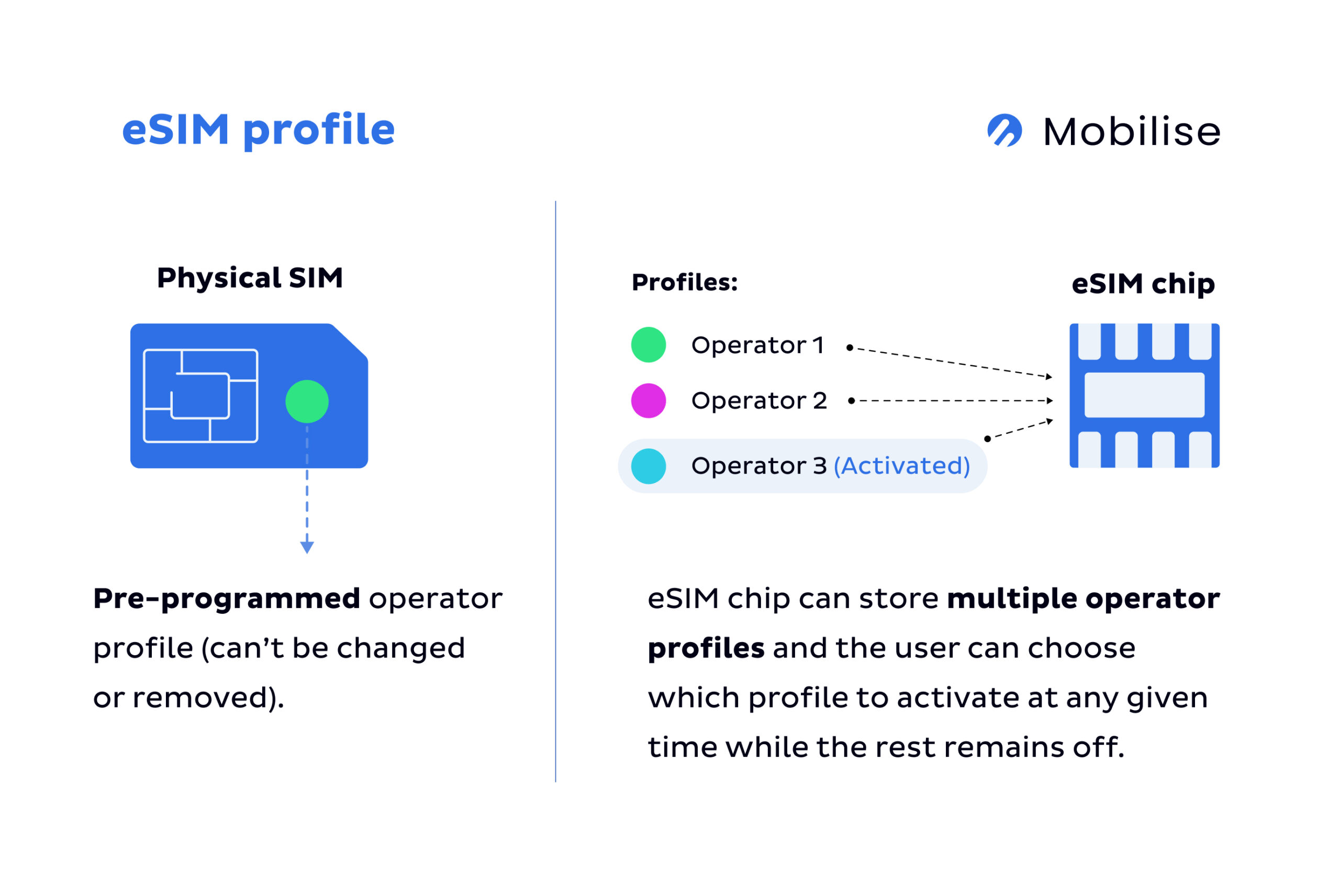
Traditional SIM is built on Universal Integrated Circuit Card (UICC) technology, just like bank cards. The UICC is a physically secure computing. However, most devices can only host one UICC card as they tend to only have one SIM slot. Some devices can hold two, they’re known as dual-SIM phones.
eUICC, or embedded UICC, is significantly smaller than the smallest SIM card – the nano SIM – and doesn’t need the space required for the SIM tray mechanics. It’s permanently embedded into a mobile device to allow users to provision operator profiles remotely. It can also hold multiple operator profiles simultaneously.
eUICC is also referred to as an eSIM chip.
The difference between eUICC vs eSIM
eSIM and eUICC tend to be used interchangeably, however, there is a clear difference between eUICC vs eSIM.
eUICC can be used interchangeably with a different term we recently talked about – an eSIM chip. However, it’s not the same thing as eSIM.
eSIM refers to the whole ecosystem – an eSIM chip with an activated eSIM profile on it. To activate an eSIM profile, a remote SIM provisioning platform is required, therefore it also makes a part of the eSIM ecosystem.
eUICC is therefore not the same as eSIM but a part of it.
Conclusion
Even though eSIM and eUICC are often used interchangeably, they are not the same thing. In fact, one is part of the other, bigger ecosystem. The wrong usage of the terms often confuses not only users but also professionals considering or working with eSIM.
We hope that this blog helped in understanding the difference. If there are any other questions you have about eSIM or any of its components, check our eSIM explained blog, where we answer the 30 most frequently asked questions about eSIM.