A lot has happened in telecoms in 2022 — mergers, regulatory changes and emerging technology. But while service providers (SPs) navigate the changes that 2022 has seen, there are also the changes of 2023 to anticipate. Here, we’ll share our predictions on the technology SPs should look to adopt in 2023 and beyond. The future of the telecom industry is here.
While many could label 2022 as a tumultuous year, there’s been plenty to shout about across the telecoms value chain. Moving into 2023, it’s certain there will be more opportunities for growth, thanks to changing regulations, the development of Web3 and the opportunities brought about by the digitalisation of telecoms services through embedded connectivity solutions.
Regulatory changes
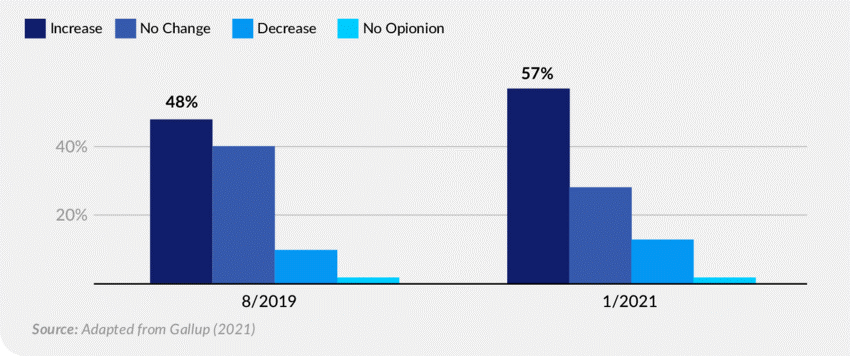
2022 has been full of regulatory changes surrounding in a bid to protect competitive technology markets. In February, the US Senate passed the Open App Markets Act, which seeks to remove the control of Apple and Google over their app stores, creating a more accessible and diverse market. Similarly, in the EU, the Digital Markets Act was entered into force in November 2022, becoming applicable from May 2023. The act will ban practices used by Big Tech that gatekeep services information. While upholding a system that eliminates competition and consumer choice.
Source: ResearchGate
Most recently, in the UK’s Autumn Budget, Chancellor Jeremy Hunt revealed that the government will bring forward the Digital Markets, Competition and Consumer Bill to Parliament before the end of the current session next summer, meaning the UK will see some progress towards regulated Big Tech in 2023.

Each of these sets of regulations stops Big Tech from implementing changes to promote their own products and services over smaller providers. As a direct result, invite much more competition to the market. More accessibility to smaller SPs will allow them to grow at a faster rate and invest and improve their platforms further. And develop new features for end users. With increased competition, a fairer market share and a wider choice, the user experience will develop to a level we’ve not yet seen as we move into 2023.
RECOMMENDED READING
MVNOs: To regulate or not to regulate? That is the question - Whitepaper
A Web3 world
A phrase first coined back in 2014 by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood, Web3 sounds like another buzzword that will pass us by. But in reality, Web3 will change how we use the internet forever. The current form of the internet that we use could be referred to as Web2. Moving forward with the future of telecom industry, we will undoubtedly see the continued development of a decentralised, more democratic version of the internet, which allows people to communicate and create content without limitations or interference from Big Tech or regulators.

Source: Myraah
If Web2 is considered two-dimensional, in that it enables reading and writing, Web3 will become three-dimensional, enabling the reading, writing and owning of content. To create this more intelligent and connected internet, we’ll need to continue developing the technologies that underlay Web3. And also consider how we use the internet will change. For example, for the metaverse to operate in its ideal way, it will require many of the features only available in Web3. Similarly, Web3 supports the use of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which are also becoming their own important element that is more than just a way of selling digital art.

So what does this mean for telecoms? Thinking of physical infrastructure, Web3 will operate similarly to the current internet in terms of servers, internet providers and every other element of the ecosystem. The change, and opportunity, for telecoms players lies in the virtual ecosystem. Web3 operates on blockchain principles to facilitate encrypted, decentralised interactions between users. Could blockchain services become a new service offering for telcos?
Embedded connectivity, the future of telecom industry
The telecoms business model is becoming more and more about creating an ecosystem of products and services. Centred around the core telecom products to drive greater customer lifetime value (CLV). This is a particularly relevant strategy today as operators are searching for ways to monetise 5G investments.
Traditional bundling strategies include internet companies adding mobile or mobile companies becoming quad play by adding TV, voice or fixed line internet to their service offering. This is becoming more sophisticated with operators broadening further in adjacent industries. Think neo-banks, ride-hailing services and travel. Embedded connectivity solutions allow the transcendence of telecoms into these industries in a much more seamless, intuitive way.

For example, connecting to the internet and roaming abroad is a double-edged sword. Take the hit of using your domestic subscription abroad or go through the hassle of sourcing and setting up a local SIM. Any business working in travel, like airlines or accommodation sites, could offer eSIMs as part of their offering, allowing customers to cover their connectivity at the same time as booking their flights and hotel. In 2023 we’ll be sure to see a growing number of applications and real-life examples where telecoms enter other markets. Offering enterprises an additional revenue stream.
While we can’t be certain of exactly what twists and turns lie ahead with the future of the telecom industry. Service providers will undoubtedly see greater opportunities, and hopefully a more level playing field, moving into 2023.