The telecom industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, with Mobile Virtual Network Enablers (MVNEs) playing a critical role in shaping the mobile ecosystem. As technology advances and consumer demands shift towards digital-first experiences, MVNEs are no longer just infrastructure providers – they are strategic enablers of innovation. But how is the MVNE market changing?
In this blog, we explore key insights from Hamish White on the evolving MVNE landscape, regulatory changes, and future opportunities.
WATCH NOW
TL;DR
- What is an MVNE? MVNEs provide the essential infrastructure that enables MVNOs to operate efficiently.
- How has the role of MVNEs evolved? The role of MVNEs is evolving beyond basic network access to cloud-based platforms, enterprise solutions, and digital ecosystems.
- How is the MVNE Market Changing? Key drivers of change include eSIM adoption, 5G, AI, and regulatory shifts that are reshaping the telecom landscape.
- Consumer expectations for digital-first, seamless, and personalised telecom services are pushing MVNEs to innovate.
- How Can Companies Gain a Competitive Edge in the MVNE Space? Embedded Connectivity is a major emerging trend, with non-telco brands integrating mobile services into their existing offerings.
- The growing demand for IoT and enterprise mobility presents untapped opportunities for MVNEs to expand beyond traditional consumer MVNOs.
What is an MVNE?
An MVNE (Mobile Virtual Network Enabler) is a company that provides the essential infrastructure and services for MVNOs (Mobile Virtual Network Operators) to launch and operate their mobile services. Unlike mobile network operators (MNOs), MVNEs don’t own spectrum or radio network infrastructure. Instead, they offer a platform with core network services like billing, customer management, and back-office systems. MVNEs act as the backbone, enabling MVNOs to deliver value in other telecom service areas, such as branding, customer acquisition, and service differentiation.

The Evolution of MVNEs
Traditionally, MVNEs focused on providing basic network access and operational support to MVNOs. However, their role has significantly evolved due to advancements in technology and shifting market demands.
Many MVNEs now utilise cloud-based infrastructures hosted by services such as AWS and Google Cloud. This transition allows for faster deployments, increased scalability, and more cost-effective operations. Initially, MVNEs provided standardised network services, but they now enable MVNOs to tailor their offerings through API-driven architectures, allowing for flexible service models and unique customer experiences.
Traditional MVNOs, such as Tesco Mobile and Giffgaff, primarily cater to consumers and focus on providing telecom services. However, MVNEs increasingly support other use cases, including IoT connectivity, private 5G networks, and enterprise solutions. Inspired by fintech companies like Revolut, MVNEs are helping brands integrate telecom services into digital ecosystems. This enables companies to offer seamless connectivity alongside banking, travel, and lifestyle services, creating a superapp experience for consumers.
I think a role that is starting to shape up for MVNEs in the coming years will be about enabling that superapp ecosystem.
Hamish White, CEO and Founder of Mobilise
The adoption of eSIM technology is disrupting the industry by eliminating physical SIM cards. This advancement facilitates new business models, enables seamless global connectivity, and reduces operational costs for MVNOs. AI tools and automation are also helping MVNEs streamline operations, automate customer interactions, and enhance network optimisation, leading to improved efficiency and customer satisfaction.
RECOMMENDED READING
How is the MVNE Market Changing?
Regulation
Regulatory changes and industry consolidation are significantly shaping the MVNE market. As mergers and acquisitions continue to gain momentum in the telecom sector, regulators are focused on maintaining competition by strengthening the MVNO business model. One approach, as seen in the UK with the Vodafone and Three UK merger, involves implementing remedies such as competitive wholesale pricing for MVNOs. Regulatory bodies like Ofcom and the CMA have introduced measures to ensure pricing remains fair for both telecom operators and MVNOs over a set period. In this, MVNEs play a crucial role in supporting these remedies, equipping MVNOs with the capabilities they need to compete effectively. As these changes continue across Europe and globally, MVNEs are increasingly positioned as key enablers in fostering a competitive telecom environment.
 Source: Vodafone
Source: Vodafone
Regulators are looking at MVNOs as a way to ensure competition after telecom mergers.
Hamish White, CEO and Founder of Mobilise
Technology
How is the MVNE market changing? The adoption of eSIM technology is eliminating the need for physical SIM cards, allowing telecom providers to embrace digital-first business models. According to GSMA Intelligence, the number of eSIM connections is expected to double between 2025 and 2030 and the global eSIM market is expected to reach a value of $19.35 billion by 2031. This shift in the telecoms industry is enabling digital-first business models, device activation and remote SIM provisioning. This is particularly beneficial for industries such as travel, logistics, and IoT, where customers require global connectivity without physical SIM card distribution.

The deployment of standalone 5G networks is transforming the telecom landscape. Enterprises across sectors such as logistics, manufacturing, and smart cities are increasingly looking to MVNEs for partnership and to provide custom 5G network solutions. Private 5G networks offer businesses enhanced security, lower latency, and greater control over network resources, making them a crucial area of growth for MVNEs.
Meanwhile, AI-driven automation is revolutionising telecom operations. AI-powered customer service tools, such as chatbots and virtual assistants, are significantly improving customer interactions and customer service in telecom while reducing costs. AI also plays a key role in predictive analytics, enabling MVNEs to anticipate network demand, prevent outages, and optimise service delivery.
Consumer Expectations
Modern consumers expect digital-first experiences similar to those provided by technology companies such as Netflix and Amazon. They demand and expect personalised and seamless digital-first experiences across all touchpoints of a brand. The expectation of a fully digital onboarding process is now a necessity rather than a luxury. And instant eSIM activation enables seamless connectivity without physical SIM cards.
Customers also require 24/7 self-service options, preferring to manage their accounts through chat features and digital interfaces rather than calling customer service agents. According to Outgrow, 74% of customers would choose a chatbot over a human agent to look for answers to simple questions. Telecom providers must offer seamless customer experiences that enable users to handle billing, plan changes, and troubleshooting without human intervention.
Hyper-personalisation is becoming a key differentiator in the MVNE space. Consumers expect personalised offers and tailored experiences based on their usage patterns and preferences. Leveraging AI and big data analytics, MVNEs can enhance customer engagement by offering targeted promotions, dynamic pricing, and customised service packages. According to PwC, since 82% of consumers are open to sharing their personal data for a more tailored experience, implementing these strategies can foster stronger engagement, leading to greater loyalty and consistent growth.
The higher the value added, the greater the chance that it will create a lasting edge.
Andrei Hagiu and Julian Wright, Harvard Business Review
Evolving Relationships with MNOs
MVNEs are transitioning from intermediaries to strategic partners in the telecom ecosystem. Traditional relationships between MVNEs and MNOs were largely transactional, with MVNEs acting as service enablers. However, MNOs are now recognising the value of MVNEs in driving innovation and reaching new market segments.
One significant shift is the rise of digital-first sub-brands, where MNOs partner with MVNEs to launch virtual networks that cater to specific customer segments. These sub-brands operate with greater agility and lower overhead costs, allowing MNOs to expand their customer base without impacting their core operations.
As the B2B sector continues to grow, MNOs are increasingly partnering with MVNEs to offer enterprise-focused solutions such as IoT connectivity, private networks, and cloud-based communications. These partnerships enable businesses to access multi-network solutions that provide seamless connectivity across different geographies and use cases.
The growing demand for Embedded Connectivity is also shaping the MVNE-MNO relationship. Companies outside the telecom industry, such as financial services and consumer electronics brands, are integrating connectivity into their products and services. MVNEs are playing a crucial role in enabling this embedded connectivity by providing seamless, scalable telecom solutions that can be integrated into non-telco ecosystems.
What Obstacles Do MVNEs Face Today?
MVNEs are facing a constantly evolving market where traditional revenue streams are under significant pressure. One of the biggest challenges stems from the commoditisation of core telecom services. Voice, SMS, and data – once billed as discrete units – are now offered in unlimited packages, making them less profitable. As a result, the margins available for MVNEs, which provide the underlying technology infrastructure for MVNOs, are becoming thinner. This trend makes it increasingly difficult for MVNEs to differentiate their offerings and sustain profitability.
Another major obstacle is the financial strain imposed by MNOs. As MNOs fight to maintain and grow their margins, they often push cost pressures down the supply chain, squeezing MVNEs in the process. Since MVNEs act as intermediaries between MNOs and MVNOs, they are particularly vulnerable to these financial pressures. Any reductions in wholesale pricing or changes in contract terms can significantly impact their ability to operate efficiently.
Furthermore, the telecom industry’s ongoing wave of consolidation presents additional risks. Mergers and acquisitions often lead to restructuring, renegotiation of contracts, and shifts in competitive dynamics that may side line smaller MVNE players. In some cases, larger telecom providers seek to bring more functions in-house, reducing their reliance on external MVNEs and further cutting into their market share. To navigate these challenges, MVNEs must focus on innovation and differentiation.
Where Are the Untapped Opportunities for MVNEs?
The MVNE sector still holds significant untapped opportunities that can drive future growth and innovation.
One of the biggest areas of opportunity lies in IoT and enterprise solutions. While many MVNEs still focus on consumer MVNOs, private networks and enterprise mobility are rapidly growing markets. Businesses require secure, scalable, and customised connectivity solutions, and MVNEs are well-positioned to provide these services, especially through private 5G networks tailored for specific enterprise needs.
Another key opportunity is in eSIM-only MVNOs, which are driving a digital-first approach in the telecom sector. eSIM significantly reduces operational costs, making it more cost-effective to acquire and serve customers. It also enables new market strategies, such as global connectivity solutions for frequent travellers, remote workers, and IoT-enabled industries.
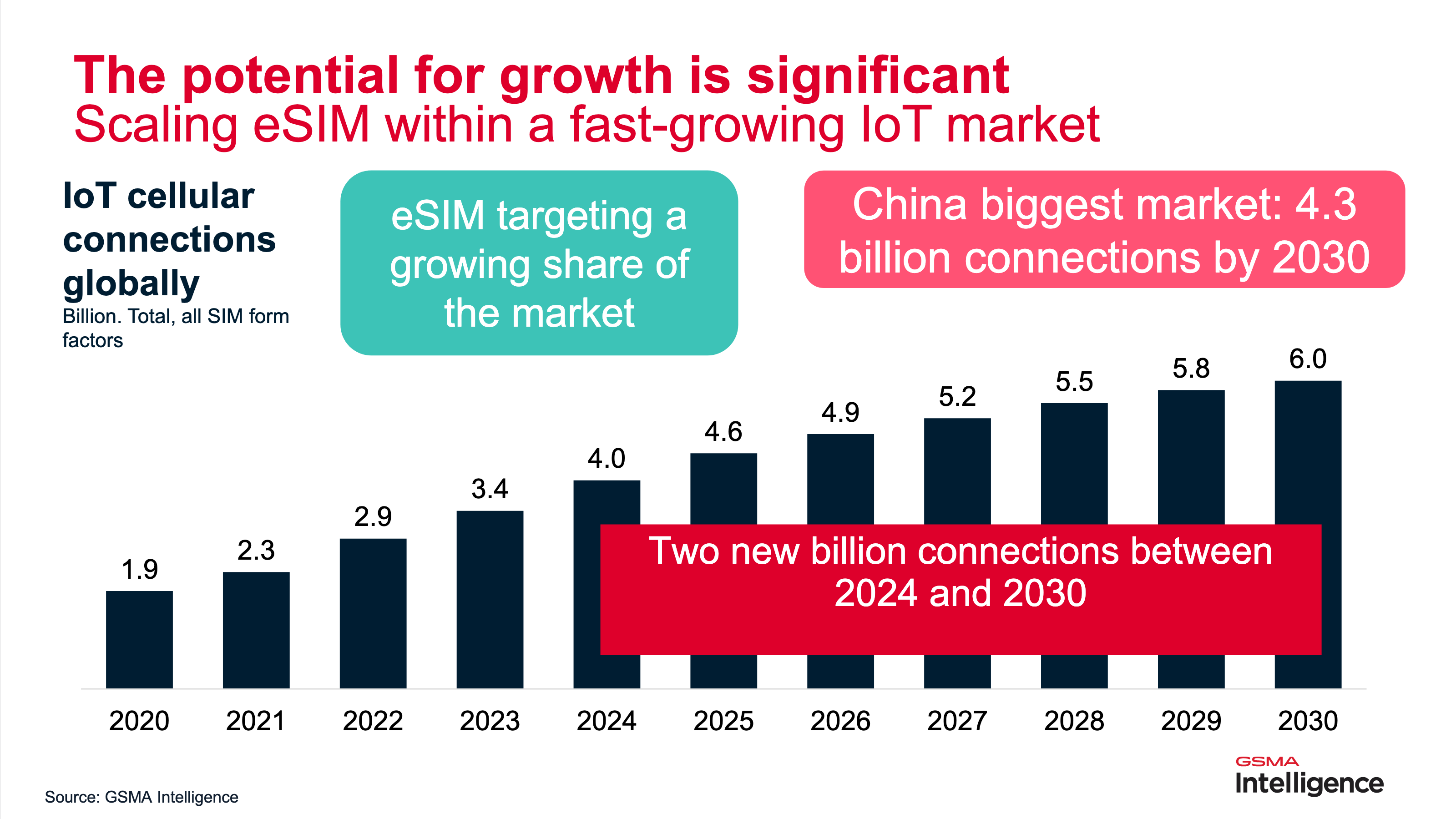 Source: GSMA Intelligence
Source: GSMA Intelligence
AI-driven solutions present another promising avenue. MVNEs have access to vast amounts of telecom data, yet many are not fully leveraging AI’s potential. AI models can bring enhanced predictive analytics, churn prediction, and optimised network usage, allowing MVNEs to provide smarter services. AI-powered intelligent agents can also be used to automate customer interactions, offering a seamless digital experience while reducing operational costs.
One of the most valuable and emerging trends is Embedded Connectivity. Non-telco brands, such as financial service providers and technology companies, are increasingly integrating connectivity services into their core offerings. Examples include Western Union integrating mobile connectivity with financial services or Revolut embedding eSIM capabilities into its banking app. By enabling these companies to offer connectivity without managing telecom infrastructure, MVNEs can unlock significant revenue streams and create stronger customer retention models.
Embedded Connectivity is particularly valuable because it allows businesses to offer seamless, value-added services while improving customer stickiness. Non-telecom companies do not want to operate telecom networks but do want to leverage connectivity as part of their offerings. MVNEs that can manage and operate this connectivity efficiently will be essential enablers of this growing trend.
A trend that’s come to the fore in the last two or three years or so is a convergence with digital services.
Hamish White, CEO and Founder of Mobilise
RECOMMENDED READING
How Can Companies Gain a Competitive Edge in the MVNE Space?
To stand out in the highly competitive MVNE market, companies must embrace key technological and strategic advancements and partnerships.
A cloud-native and API-first approach is essential for success. Partnerships with cloud-native platforms allow MVNEs to leverage the scalability, redundancy, and flexibility offered by providers like AWS and Google Cloud. This ensures efficient deployment, enhanced service reliability, and cost-effective scaling during peak demand. API-first architectures further differentiate MVNEs by enabling seamless integration with third-party systems, allowing businesses to build customised solutions on top of telecom infrastructure.
Embedded Connectivity and eSIM support are also crucial differentiators. MVNEs must focus on exposing core telecom infrastructure through APIs, allowing brands to integrate connectivity services effortlessly into their ecosystems. Mobilise, for example, offers a fully developed Embedded Connectivity solution using eSIM, enabling businesses to embed telecom services into their existing product offerings.
eSIM really enables new business models, and those new business models will have implications on the technology strategy for MVNEs going forward.
Hamish White, CEO and Founder of Mobilise
Automation and AI-driven efficiency are becoming indispensable in the telecom industry. AI-powered automation streamlines operations enhances customer service and optimises network management. Agentic AI solutions, capable of handling customer inquiries and automating backend processes, will be key drivers of operational efficiency and cost reduction for MVNEs.
Digital-first customer experience in telecom industry is another priority. Many traditional telecom vendors remain network-driven, neglecting the importance of seamless digital onboarding. Companies must excel in digital transformation by offering fully automated eSIM onboarding, self-service options, and AI-enhanced customer interactions to meet evolving consumer expectations.
Multi-network support is emerging as a game-changing capability. With the rise of travel eSIMs and global roaming services, MVNEs must aggregate multiple MNO networks to provide uninterrupted connectivity worldwide. The ability to dynamically switch between MNO profiles based on price, quality, and availability allows MVNEs to offer flexible, high-quality coverage for consumers and enterprises.
Conclusion
So, how is the MVNE market changing? To conclude, it’s currently at a turning point, driven by eSIM, 5G, AI, and digital transformation advancements. While challenges like cost pressures and market consolidation persist, new opportunities in IoT, embedded connectivity, and automation are reshaping the industry. MVNEs that embrace innovation and build strategic partnerships will be best positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.
Interested in learning more about how Mobilise is driving digital transformation in the MVNE space? Explore our MVNE Platform today!