The evolution of eSIM has been nothing short of transformative, reshaping the telecom industry and consumer expectations for mobile connectivity. Starting as a solution for IoT devices in 2010, eSIM has quickly grown into a mainstream technology, now available in smartphones, tablets, wearables, and more. With the ability to be remotely activated and managed, eSIM provides unmatched flexibility for both consumers and operators. This blog dives into eSIM’s journey from its inception to its growing role in the consumer market, exploring the advantages, industry impact, and eSIM future trends shaping its adoption.
TL;DR
- Is eSIM the Future? Yes! With growing adoption and affordability, eSIM is set to become the industry standard, with applications across smartphones, wearables, IoT, and beyond.
- Evolution of eSIM: Launched in 2010 for IoT devices, embraced by Apple and Google in 2016–2018 for consumer devices, and now widely adopted.
- Predictions and Trends: eSIM-compatible devices to surge, new applications in travel, and ecosystem growth through industry partnerships.
- Benefits for Consumers: Flexible carrier switching, multi-device connectivity, better security, and reduced roaming costs.
- Benefits for Operators: Reduced logistics costs, digital-first onboarding, new revenue streams, and enhanced customer experience.
Understanding the Evolution of eSIM
Before we head on to discuss the future of eSIM in the consumer market, let’s quickly recap on its evolution so far.
The journey of eSIM began in 2010 within the IoT sector, where it was introduced to simplify connectivity in unmanned or hard-to-access devices. Unlike physical SIM cards, eSIMs are embedded into devices and can be reprogrammed remotely. Recognising its potential for consumer devices, Apple advocated for eSIM, seeing the opportunity to reclaim valuable device space. The small eSIM chip, nearly half the size of a nano SIM, aligned well with Apple’s drive to design ever-sleeker devices.
Despite early concerns from the GSMA around security, the organisation approved eSIM for consumer use in 2016, sparking new developments in mobile technology. Google was the first to release an eSIM-compatible handheld device, the Pixel 2, in 2017. Apple quickly followed suit with the iPhone XR and XS, rapidly expanding its eSIM-capable device lineup. However, Apple’s eSIM-only iPhone 14 release in the US in 2022 drew widespread attention, significantly boosting consumer awareness of eSIM.
RECOMMENDED READING
When did eSIM come out? Who invented eSIM? - The history of eSIM
Impact of eSIM Adoption on Telecommunications
Operators initially met the introduction of consumer eSIM technology with hesitation. Many feared it would make switching providers too easy, potentially increasing churn rates. Unlike traditional SIM cards, which require a physical change to switch carriers, eSIMs can be remotely activated and reprogrammed, simplifying the switching process and shifting control away from operators that traditionally relied on physical SIM cards to maintain customer loyalty.
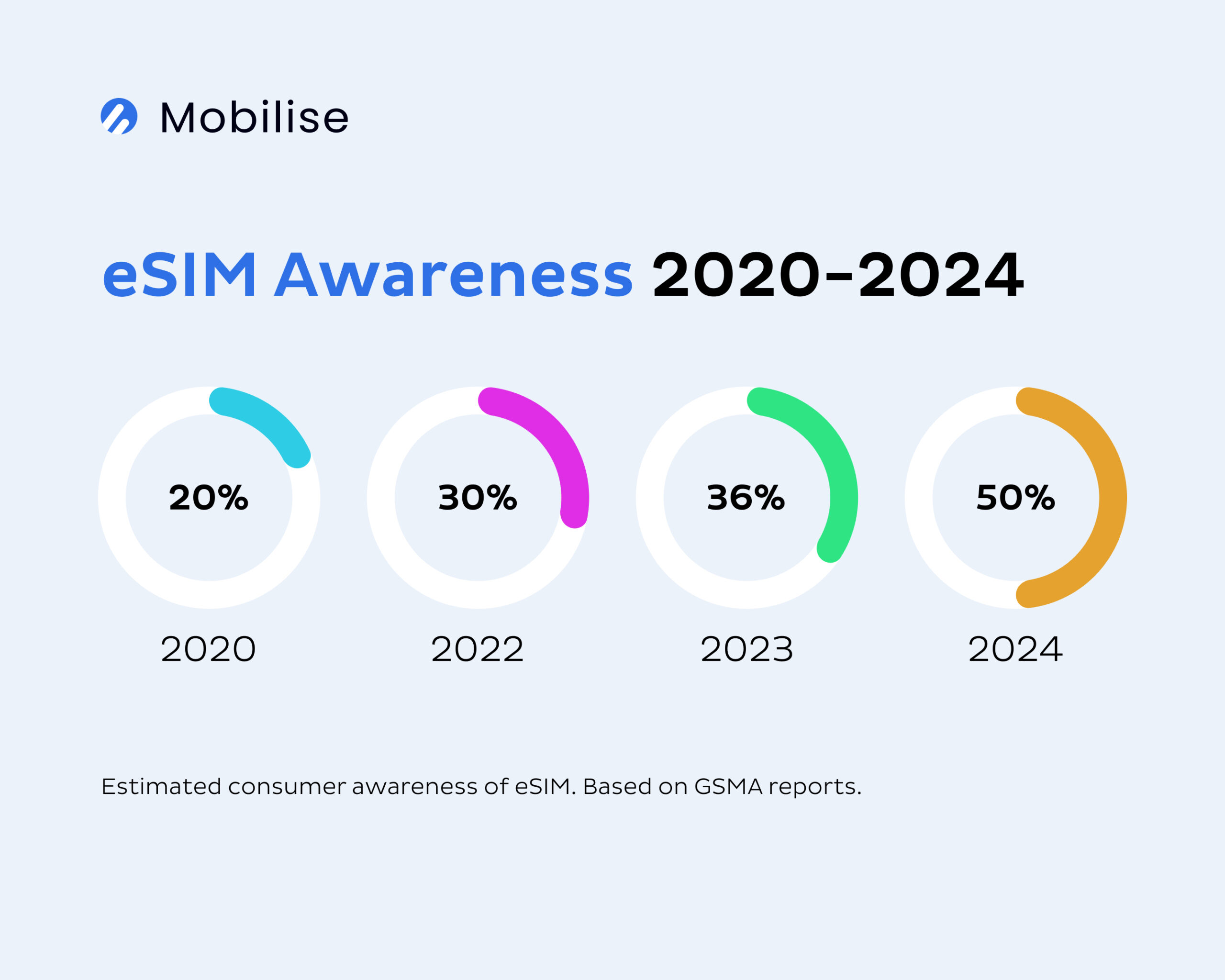
Additionally, operators cited low consumer awareness of eSIM as a barrier to adoption, creating a “chicken and egg” scenario: operators hesitated to launch eSIM offerings due to low awareness, yet consumers typically learn about telecom advancements through their providers or device manufacturers. With limited support from less than 10% of OEMs (original equipment manufacturers) and even fewer operators, awareness remained low. However, some operators, like Vodafone, took proactive steps by offering free eSIM trials at major events, such as Glastonbury and Boardmasters (source). Their efforts have yielded results, with Vodafone recently reporting that one in three new customers in the past year has adopted eSIM.
Over the years, operators have gradually shifted their approach. Recognising the demand for digital, flexible services—driven by the rise of eSIM-only apps, travel eSIM providers, and an increasing number of eSIM-capable devices at accessible prices—many telecom providers have adapted to eSIM. They now see it as an opportunity to innovate, streamline customer onboarding, and support multi-device plans across wearables, tablets, and smartphones.
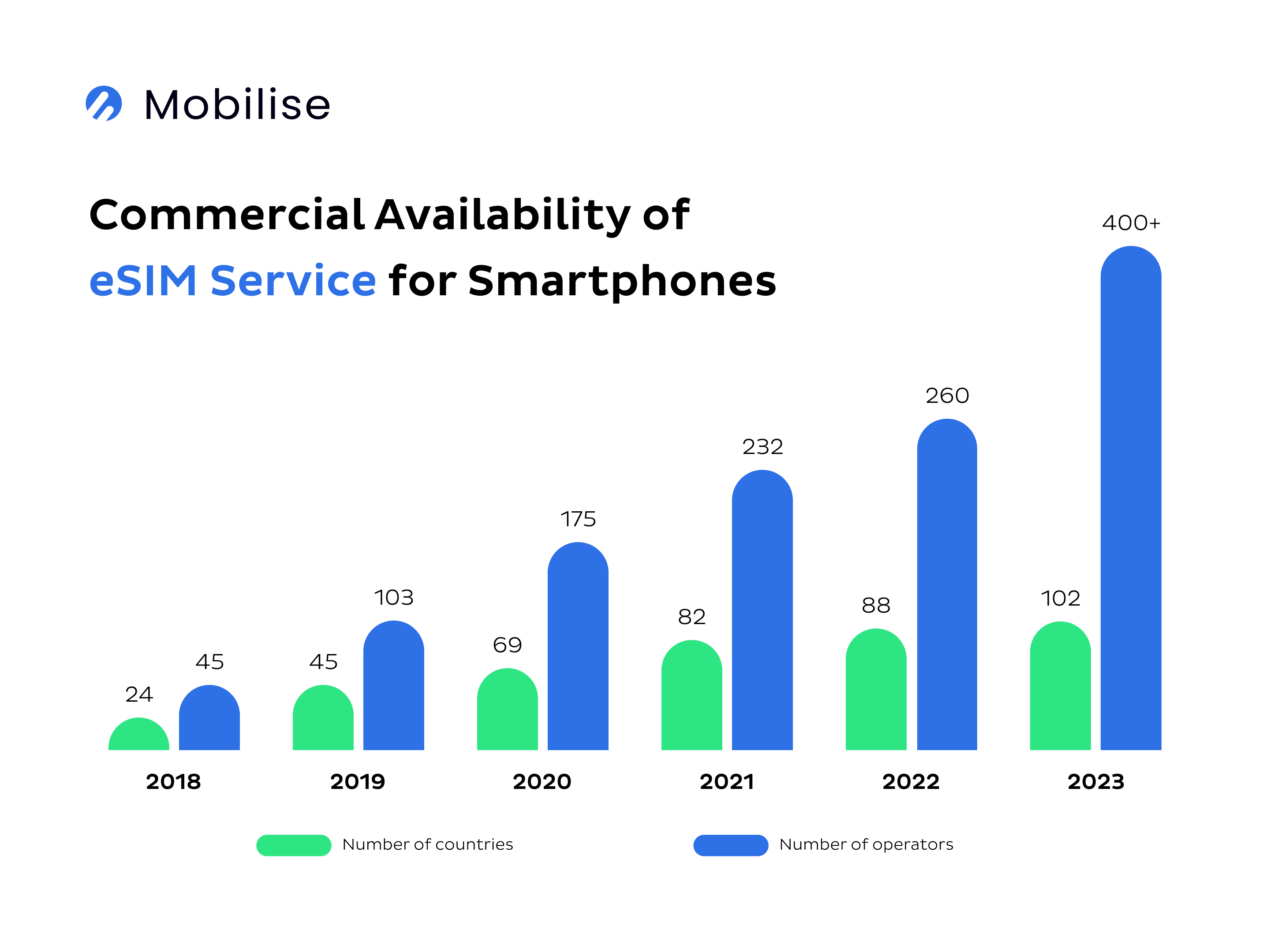
While some operators remain cautious about churn risks, many have embraced eSIM as a way to differentiate their services and enhance customer experience in telecom. Today, telecoms increasingly view eSIM as a strategic advantage, unlocking new revenue streams and enabling flexible, digitally driven mobile solutions that improve customer satisfaction.
Advantages of eSIM over Traditional SIM Cards
eSIM offers a wide range of advantages, benefiting both consumers and operators alike. While it presents particular challenges, which are described in more detail in our consumer eSIM white paper, the benefits make a strong case for adoption.
For consumers, eSIM provides flexibility, easier carrier switching, multi-device connectivity, and enhanced security—all key factors driving demand.
For telecom providers, eSIM offers a pathway to digital-first services, lower operational costs, and new revenue streams through travel and multi-device plans.
Weighing both the pros and cons, it’s clear that implementing eSIM is a strategic move for telecom providers, as it can drive customer satisfaction and significantly boost their bottom line through innovative service offerings and streamlined operations.
eSIM Advantages for Consumers
- Easy Setup and Activation: Activation is often done digitally via apps or QR codes, making it fast and seamless.
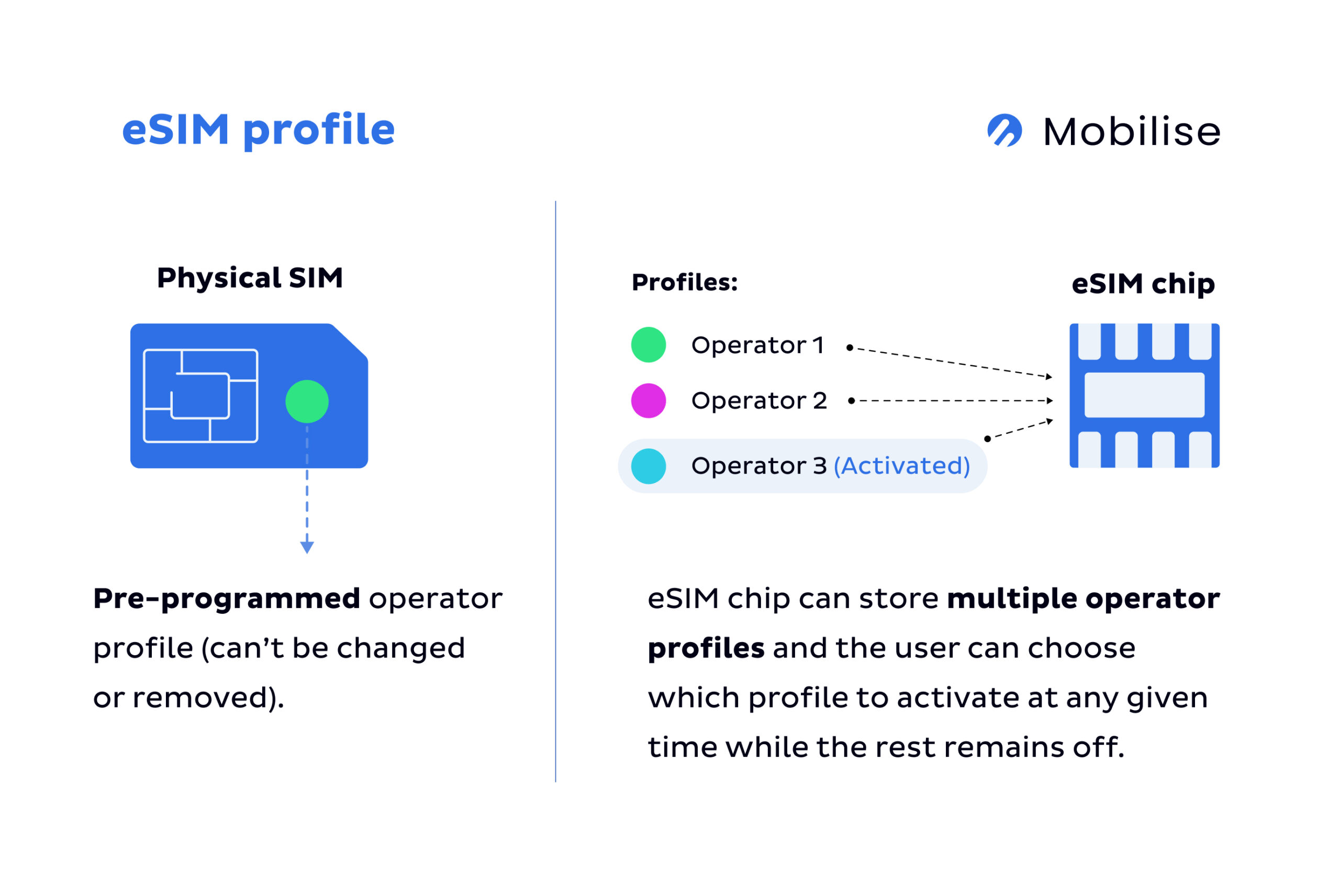
- Multiple Profiles on One Device: The eSIM chip enables storing multiple carrier profiles on one device, which is ideal for managing personal and business lines or international travel.
- Reduced Roaming Costs: Consumers can easily activate local eSIM plans when travelling, reducing the need for roaming fees.
- Convenient Carrier Switching: Allows consumers to switch carriers without needing a physical SIM, making it faster and more convenient.
- Improved Security: If a device is lost or stolen, eSIMs are more complicated to remove, offering an added layer of security through enhanced eSIM security measures.
- Environmental Benefits: Reduces plastic waste since there is no need for physical SIM cards, contributing to greener choices.
Advantages of eSIM for Operators
- Lower Operational Costs: Reduces the need for physical SIM logistics, such as manufacturing, shipping, and distribution.
- New Revenue Streams: Enables innovative offers like data bundles for travellers, multi-device plans, and temporary plans for events or short-term needs.
- Reduced Churn Risk: Operators can bundle eSIM with multi-device plans, increasing customer retention through flexible, value-added services.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Allows operators to offer a more seamless, digitally driven experience, meeting modern consumer expectations.
- Broader Market Reach: This makes it easier to offer global or region-specific plans without the need for a local physical presence.
- Data-Driven Insights: Digital provisioning provides more data on user behaviours and needs, enabling tailored offers and better customer insights.
Is eSIM Future the way?
And finally, we’ve arrived at the key question of this article. And the short answer is yes, eSIM is the future.
With projections indicating continued growth at CAGR (compound annual growth rate) between 7% and 10.2% from 2022 to 2030 and widespread adoption across the mobile industry, the future of eSIM technology looks promising. By 2025, the global eSIM adoption rate across smartphones will be between 25% and 40%, a testament to the increasing demand for flexible, digital-first connectivity solutions. Moreover, market trends reveal that eSIM is expanding in smartphones and rapidly gaining traction in other devices like tablets, wearables, and even cars, with eSIM-enabled wearables projected to exceed 100 million units by mid-decade.
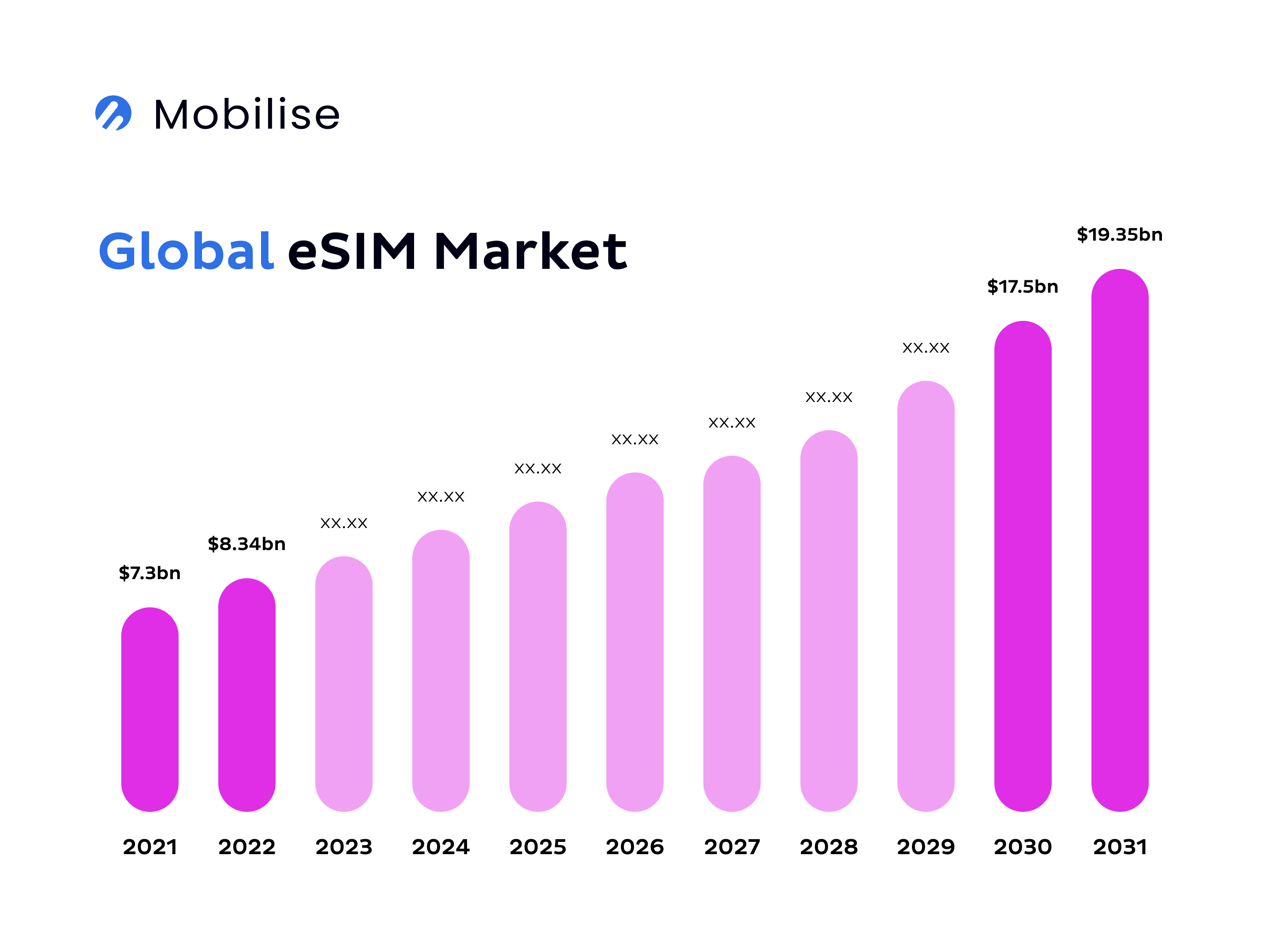 Source: Mobilise, based on Straits Research
Source: Mobilise, based on Straits Research
As eSIM evolves, new and innovative applications are emerging. From enabling seamless travel connectivity with local plans to supporting IoT applications in smart homes and autonomous vehicles, eSIM unlocks diverse use cases beyond traditional mobile needs. The versatility of eSIM is also paving the way for innovative business models, such as travel-specific eSIMs and pay-as-you-go plans that cater to users looking for on-demand connectivity.
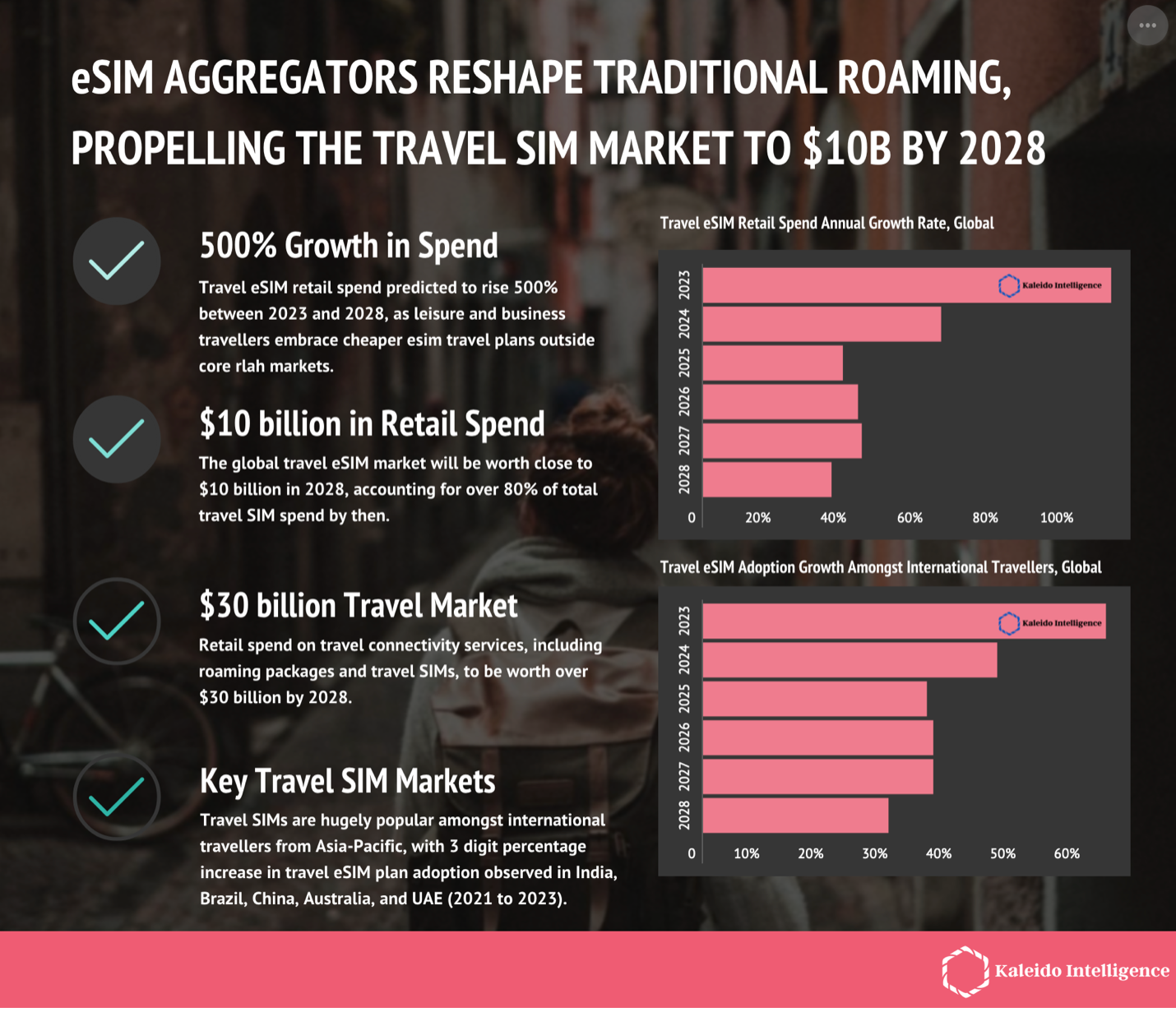 Source: Kalleido Intelligence
Source: Kalleido Intelligence
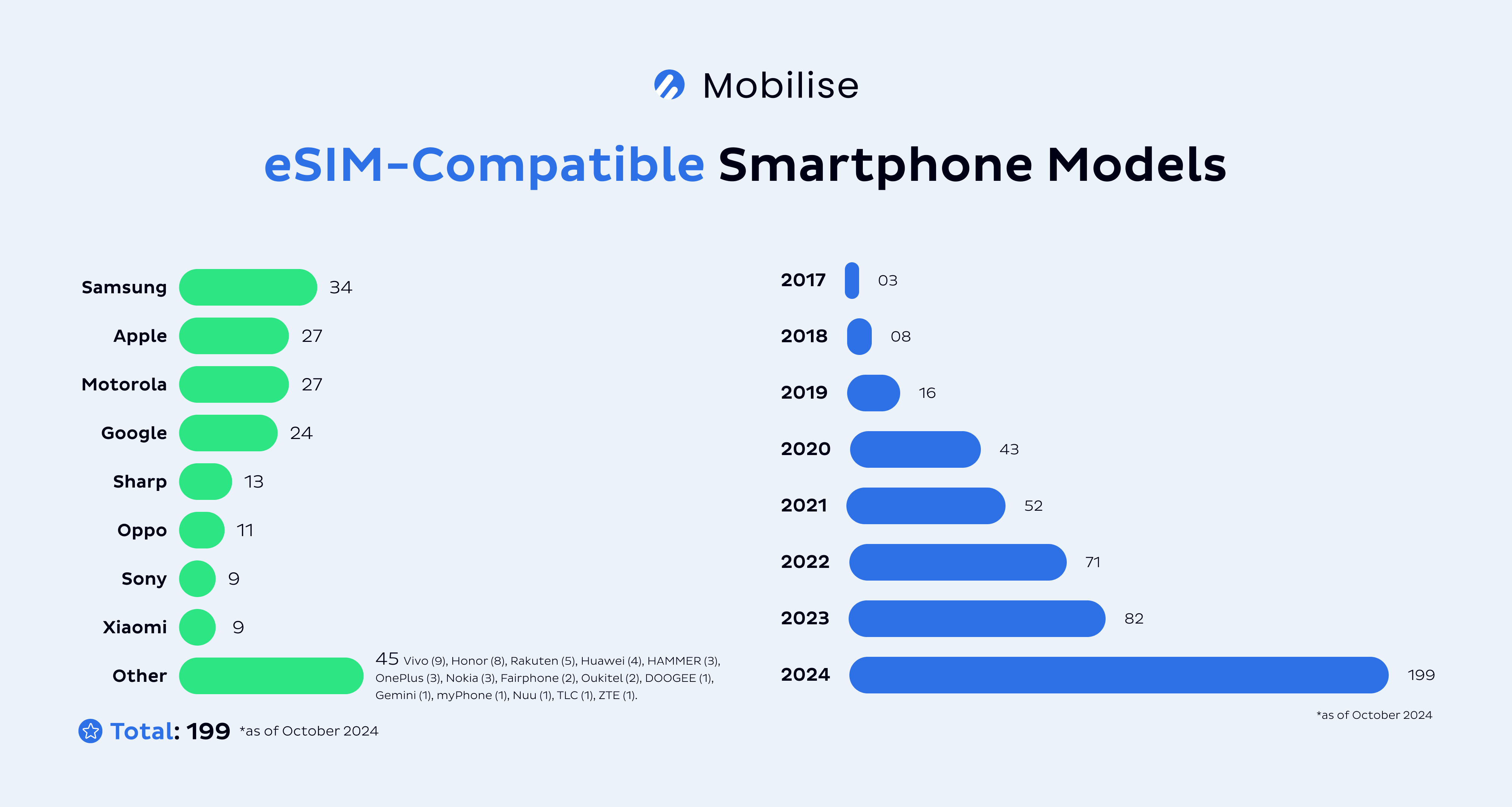
Another critical factor in eSIMs’ future is its growing affordability. As eSIM-compatible devices become more accessible, it’s anticipated that the technology will no longer be limited to high-end models, making it available to a broader audience. In our recent blog about our picks for the most affordable eSIM-compatible phones, we uncovered that the lowest price in 2024 hovers at around £199, resulting in a £200 drop from 2023, when the cheapest eSIM phone was around £399. This increased accessibility is expected to drive a surge in eSIM adoption, particularly in emerging markets.
Collaboration within the eSIM ecosystem is also accelerating growth. Partnerships between telecom operators, device manufacturers, and eSIM providers foster a supportive environment for eSIM expansion, which enhances interoperability and ensures robust support for consumers worldwide. With major tech brands, including Apple, Google, and Samsung, pushing eSIM in their latest devices, the technology is well-positioned to become the industry standard for connectivity. We’re proud to announce that Mobilise has been recognised as a Challenger in the 2023 eSIM Orchestration Rankings by Counterpoint Research, highlighting our commitment to delivering robust and innovative eSIM solutions and streamlining eSIM implementation.
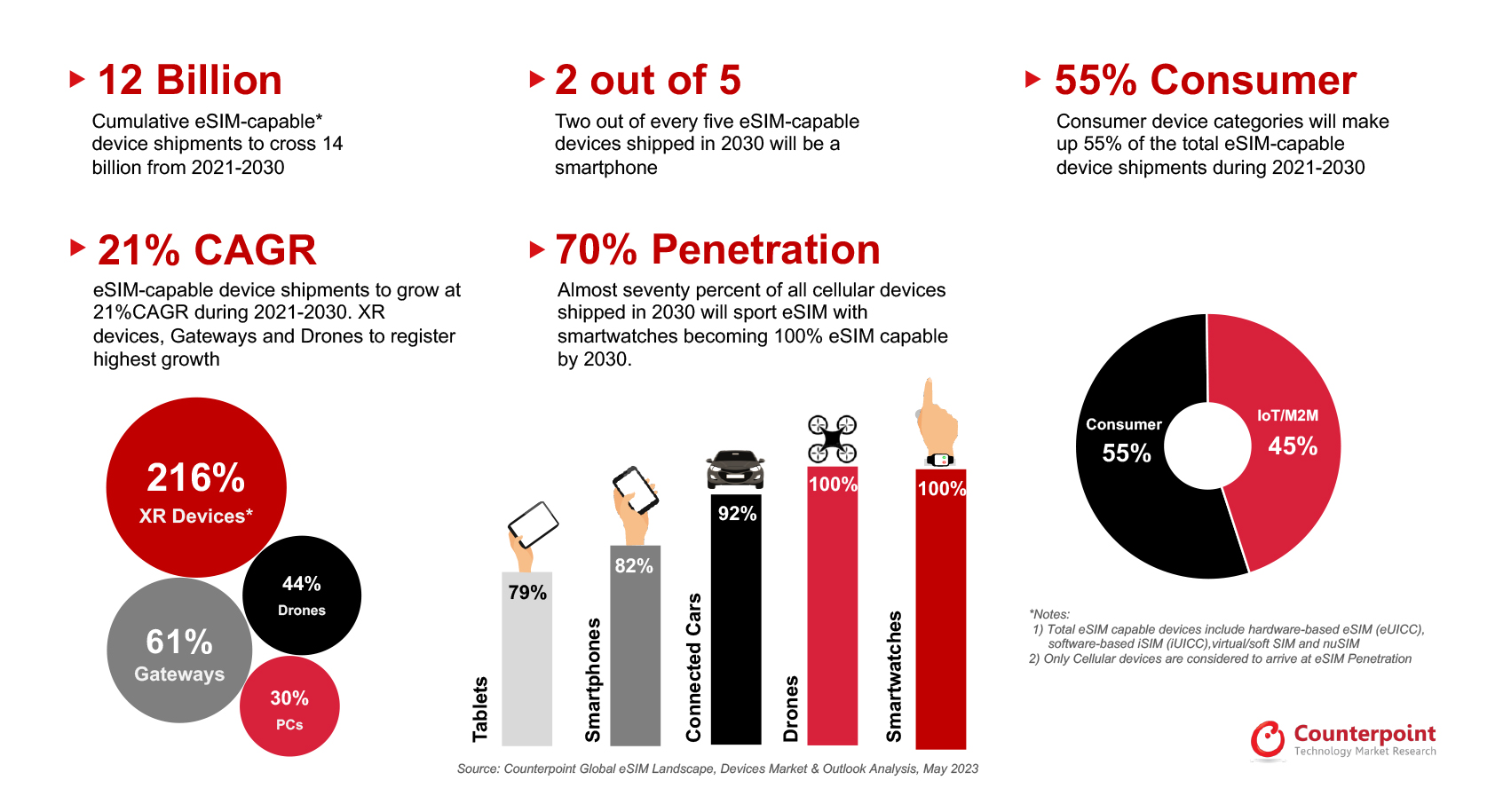 Source: Counterpoint
Source: Counterpoint
These trends underscore eSIMs’ role as a key driver in the digital transformation of mobile connectivity, offering a future where seamless, flexible, and innovative solutions redefine how consumers connect.
RECOMMENDED READING
Conclusion
As eSIM continues to mature, its impact on mobile connectivity is clear. The technology’s flexibility, cost-efficiency, and adaptability to various consumer devices have driven its adoption globally, transforming both user experiences and telecom operations. With projections of exponential growth and the expansion of eSIM-compatible devices, the future looks promising for eSIM as it becomes increasingly accessible and affordable. Collaboration among operators, device manufacturers, and technology providers further strengthens the eSIM ecosystem, paving the way for a fully digital, seamless, and secure mobile experience. eSIM isn’t just a trend—it’s setting a new standard in connectivity that is here to stay and evolve.
Need help with your eSIM service offering? Click here to find out more about eSIM as a Service and our eSIM SDK solution, or contact us now to book a demo!