In the last few years, eSIM has become a telco buzzword – widely discussed, marketed, and publicised. And the recent rumours of an eSIM-only iPhone 15 to be released in Europe have only brought the technology further into the spotlight. Consumers have a common concern: eSIM security.
But what is eSIM?
Embedded Subscriber Identity Module (eSIM) is a digital SIM with the same function as a plastic SIM card. But it’s physically integrated into the device. In other words, it can’t be removed from the device and replaced with another SIM. It’s activated remotely which allows operators to move their entire customer journey online.
RECOMMENDED READING
Thanks to the convenience of the technology and Apple’s release of the eSIM-only iPhone 14 in the US and Canada, it’s become increasingly popular. However, with this convenience comes the need for robust security and privacy measures to protect users’ sensitive information. Ensuring the security and privacy of eSIM data is crucial in preventing unauthorized access, data breaches, and other forms of instances that could compromise users’ personal and financial information.
Even though eSIM is taking the industry by storm, is it really more secure than physical SIM cards?
How does eSIM technology work?
The main difference between eSIM and traditional SIM cards is that an eSIM doesn’t come with an operator’s profile data pre-installed in the device. It’s a programmable SIM that’s embedded in a device, allowing users to switch between mobile network operators without physically changing SIM cards. It typically consists of a hardware chip that stores the SIM data, as well as software and protocols that enable remote management of the eSIM profile.
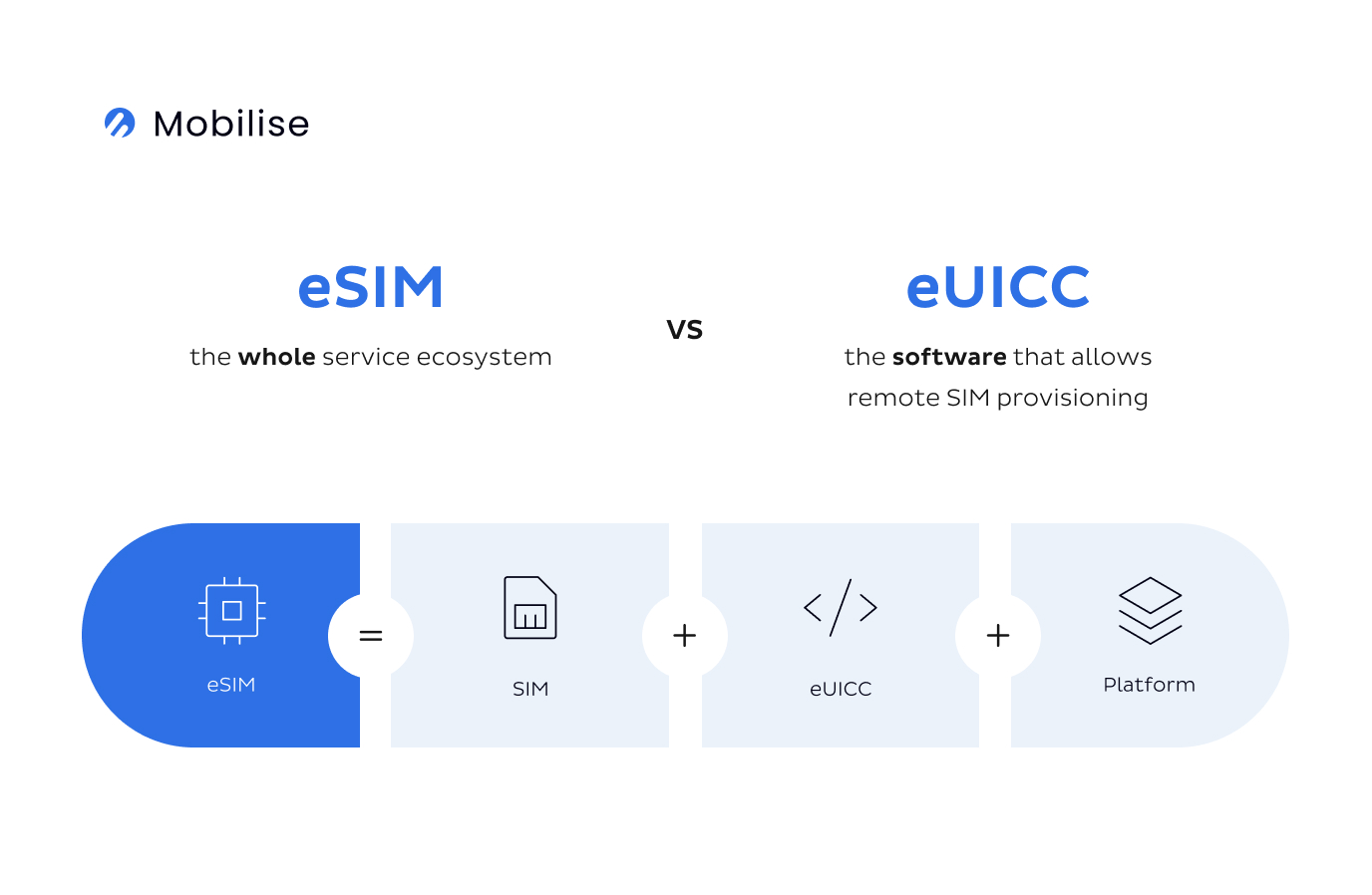
eSIM architecture
This functionality of Remote SIM provisioning (RSP) allows for secure operator profile management. Including the authentication and activation of embedded SIMs and their enabling, disabling and deleting. It completely removes the need of swapping single-profile physical SIM cards. The process can take as little as one tap and less than 60 seconds for a profile to activate.
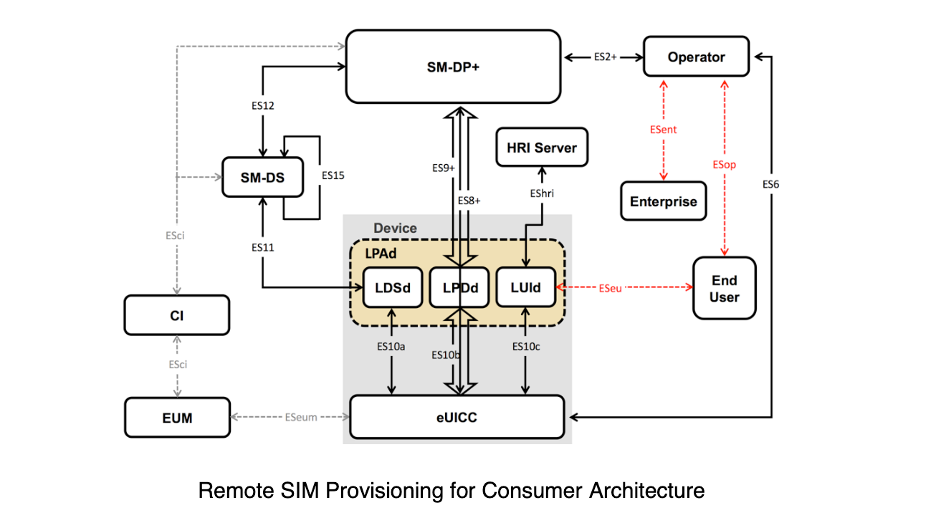
GSMA’s Consumer Remote SIM Provisioning
GSMA’s Consumer solution was developed on the basis of the M2M solution with the needs of end-users in mind. The main elements involved: the SM-DP+ (Subscription Manager – Data Preparation +). The SM-DS (Subscription Manager – Discovery Server). The LPA (Local Profile Assistant) and the eUICC (Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card).
 Source: GSMA
Source: GSMA
SM-DP+: The creation, download, remote management (enable, disable, update, delete) and protection of operator credentials (the Profile). These are all handled by the SM-DP+. It has the + designation because it combines the functions of both the SM-DP and the SM-SR of the M2M solution.
SM-DS: This provides the necessary mechanisms to notify the local discovery service within a device that the SM-DP+ element wants to communicate with it. The element sends an event registration message to the SM-DS for a target consumer device.
LPA: The LPA assists with the download of profiles. And secures the end-user interface on the device that is used for local control.
eUICC: People often assume it’s the eSIM that has remote provisioning capabilities but that’s not the case. eUICC is the chip that hosts the profile that can be provisioned remotely by the operator.
Why is eSIM security important?
Like any technology, eSIMs also have certain risks and vulnerabilities. Some of the potential risks include the possibility of malicious actors intercepting and manipulating eSIM communications. Exploiting vulnerabilities in eSIM software or hardware, and gaining unauthorised access to sensitive user data stored on the eSIM chip. Additionally, eSIMs can also be subject to social engineering attacks or other forms of user error. Such as inadvertently exposing login credentials or failing to update software regularly.
Hackers and cybercrime pose a significant threat to the security and privacy of eSIM technology. They could attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in eSIM hardware and software to gain access to user data or intercept eSIM communications. Cybercriminals may also attempt to use phishing or other social engineering tactics to trick users into revealing their eSIM login credentials or other sensitive information. Furthermore, eSIMs may also be targeted by ransomware attacks or other forms of malware that could compromise user data or device functionality.
Protecting personal and sensitive data is critical to prevent identity theft, financial fraud, and other forms of cybercrime. Personal information such as names, addresses, and social security numbers can be used to commit identity theft. While financial information such as credit card numbers and bank account details can be exploited. On top of this, sensitive data such as healthcare information, legal records, and intellectual property can also be targeted by cybercriminals seeking to compromise the privacy and security of individuals or organisations.
eSIM security offers several advantages over physical SIM security, such as better protection against physical theft or loss, as well as the ability to remotely manage and update eSIM profiles. However, eSIMs may also be subject to unique security challenges, such as the potential for remote attacks and the need for robust encryption and authentication protocols. Overall, both physical and eSIMs require appropriate security measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of user data.
How to ensure eSIM security?
Securing eSIM technology involves several best practices, such as choosing a trusted mobile network operator, using strong and unique passwords for eSIM profiles, keeping eSIM software up-to-date, and avoiding public Wi-Fi when managing eSIMs. Additionally, users should be cautious of suspicious emails or messages that request eSIM login credentials or personal information. It’s also essential to regularly monitor eSIM activity and report any suspicious activity to the relevant authorities.
Mobilise can help!
Working with a trusted eSIM provider like Mobilise offers several benefits. Such as access to secure and reliable eSIM technology, support for multiple mobile operating systems, and compliance with industry standards and regulations. Working with a trusted eSIM provider can help ensure a seamless and user-friendly fully digital experience. Enabling end-users to easily activate and manage their eSIMs without encountering technical issues or security concerns.
Mobilise’s eSIM as a Service platform allows service providers to capitalise on eSIM technology to offer consumer eSIM capabilities to their customers quickly and efficiently. eSIM as a Service comes as a white-labelled eSIM app. Thanks to our strategic partnerships, the platform offers eSIM DP+ infrastructure that is compliant with SAS-SM certification by the GSMA.
With these functions, mobile network operators (MNOs) and mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs) of all sizes can embrace the opportunities created by eSIM technology and form entirely digital journeys for their subscribers.
Is eSIM more secure than physical SIM?
A comparison of security between eSIMs and physical SIMs reveals that eSIM technology offers better protection against physical theft or loss. As well as the ability to remotely manage and update eSIM profiles. eSIM technology is far more secure due to stronger encryption and remote management capabilities. Allowing users to manage their eSIMs without the need for physical access.
However, there are a few criticisms towards the security of eSIM. This includes the potential for remote attacks and the need for robust encryption and authentication protocols. There have been several cases of eSIM security incidents that concern eSIM swapping attacks, leading to hacking, fraudulent activities, and identity theft.
Addressing these concerns requires implementing best practices. This includes choosing a trusted mobile network operator, using strong and unique passwords for eSIM profiles, and keeping eSIM software up to date. Ongoing security assessments and improvements are also critical to ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of eSIM data, and eSIM providers should remain vigilant in monitoring and addressing potential security risks.
GSMA recognises the importance of eSIM security and compliance and has put into place requirements for security assurance, functionality, and interoperability.
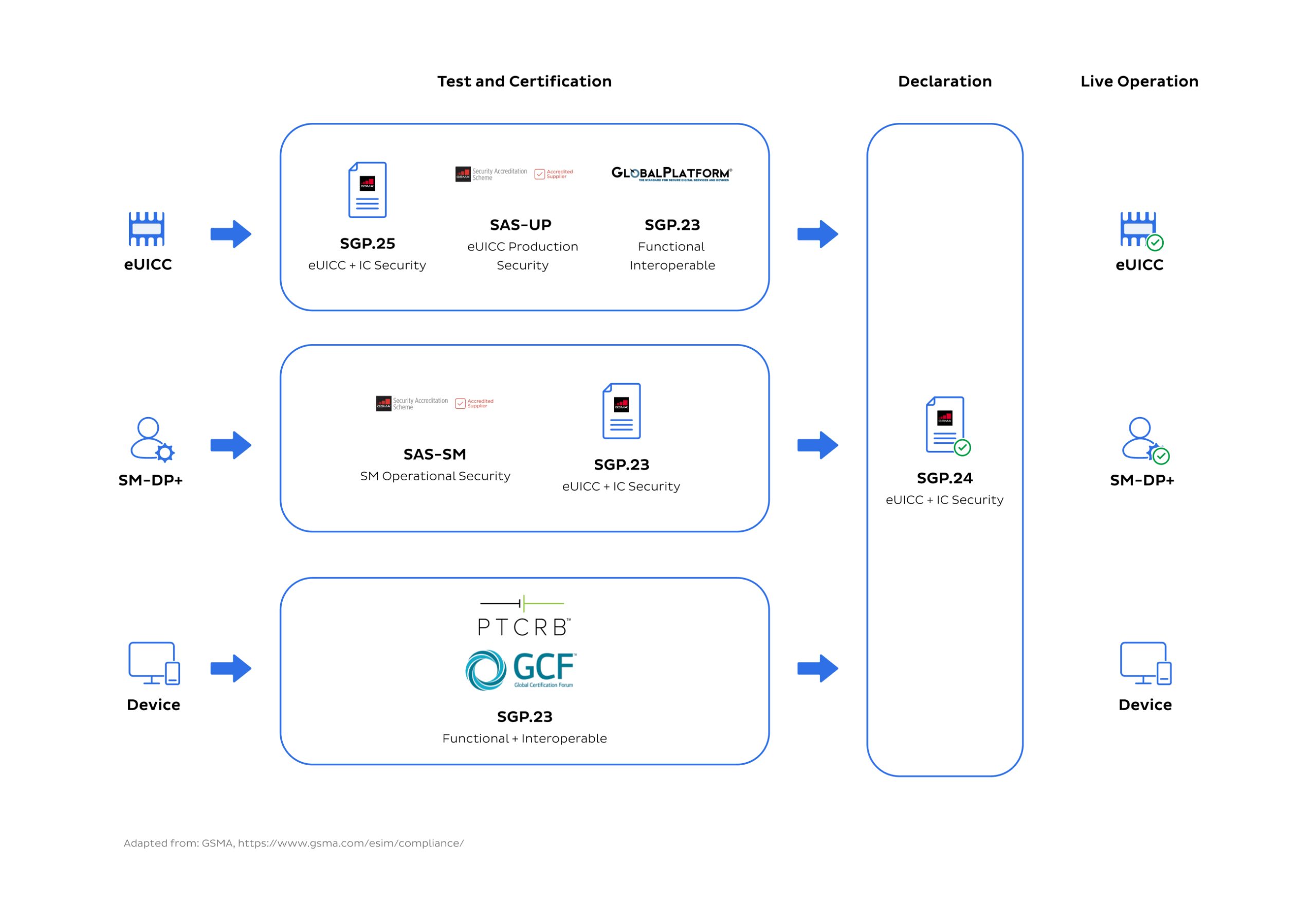
eSIM security and privacy regulations
There are multiple regulations around eSIM security and privacy. One of which is the EU Commission’s GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). It requires eSIM providers to implement appropriate technical and security measures to protect user data, ensure EU citizens’ privacy rights, and define legal obligations for the adequate control and processing of data. In the US, five states -California, Virginia, Colorado, Utah, and Connecticut, will launch new comprehensive consumer privacy laws. This comes following California’s recent second issue of the California Privacy Rights Act.
Compliance requirements may include conducting regular risk assessments and implementing appropriate access controls and encryption measures. And maintaining detailed records of eSIM activity.
Conclusion
While eSIM is not new by any means. It’s an exciting piece of technology that still requires the same level of security and regulation as traditional SIM cards. Service Providers both in and outside of the telco industry need to ensure that they work with a trusted eSIM provider. All to ensure the protection and privacy of their customers and eSIM security.