Connectivity is a necessity. And eSIM technology has emerged as a promising solution to both consumers and service providers, offering the potential to revolutionise how we stay connected. So why is eSIM not popular?
Despite its numerous advantages, from seamless switching between networks to enhanced security features, eSIM adoption has been slower than anticipated. In this blog, we’ll cover the reasons behind the slow uptake of eSIM and explore the challenges and opportunities it presents.
TL;DR
- eSIM faces many hurdles to popularity, including:
- Resistance from traditional players
- Lack of consumer awareness
- Regulatory hurdles
- Cost considerations
- Complex implementation
- Security and privacy concerns
- Efforts between stakeholders and innovative solutions can pave the way for wider eSIM adoption.
Resistance from Traditional Players
The telecoms industry has been slow to embrace eSIM. And it could stem from multiple perceived threats against their core businesses.
The main reason why traditional players are resistant to adopting consumer eSIM technology is because they see it as a threat to their current business models. Telecom operators are particularly concerned about reduced SIM card sales and the possibility of losing long-term subscriber contracts, which could significantly affect their revenue streams and profitability. These operators have invested significant resources in infrastructure and marketing strategies based on the traditional SIM card model, making it difficult for them to fully embrace a technology that fundamentally alters the dynamics of customer engagement and retention dynamics.
eSIM has the potential to give consumers more flexibility and control over their connectivity options, which poses a direct challenge to the traditional strategy of locking customers into long-term contracts. Operators are worried about losing the ability to control subscriber churn and may struggle to adapt their pricing and service offerings to compete in a more dynamic and fluid market.
Device manufacturers are also hesitant to adopt eSIM technology due to concerns about its potential impact on their business models. Integrating eSIM technology into devices requires significant research, development, and testing investment, with no guarantee of widespread adoption or acceptance from consumers. Manufacturers must weigh the potential benefits of eSIM, like reduced device complexity and enhanced user experience, against the risks of alienating telecom partners and disrupting existing supply chain dynamics. Ultimately, the fear of the eSIM experience is driving traditional players away from adopting eSIM.
Opportunities for collaboration and partnerships
Despite initial resistance, there are significant opportunities for collaboration and partnership between traditional players and eSIM providers. By working together, telecom operators, device manufacturers, and eSIM providers can leverage their strengths to drive market adoption and innovation.
Partnering with eSIM providers also offers telecom operators the chance to differentiate their services, attract new customers, and tap into emerging revenue streams, such as IoT connectivity and enterprise solutions. By embracing eSIM, operators can position themselves as innovators in the evolving telecommunications landscape and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Device manufacturers can also team up with eSIM providers to enhance the value proposition of their products and differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace. By integrating eSIM functionality into their devices, manufacturers can offer consumers greater choice, flexibility, and convenience while reducing the complexity and cost of device management.
Moreover, collaboration between traditional players and eSIM providers can drive digital identity, authentication, and security innovation. By combining their expertise and resources, stakeholders can develop new use cases and applications for eSIM, unlocking new opportunities for revenue generation and market expansion.
Lack of Consumer Awareness
The lack of eSIM awareness and its benefits poses a significant barrier to adoption. Educating consumers about eSIM functionality, such as remote provisioning and network flexibility, is crucial. Telecom SaaS providers can play a vital role in raising awareness through targeted marketing campaigns and educational initiatives.
There are a few reasons why consumer awareness of eSIM is so low despite its long existence. However, the main issue lies on the OEMs’ and SPs’ sides.
As shown in the image below from a GSMA Intelligence report, only 15% of consumers were aware of eSIM from an OEM, and only 8% received information from their mobile phone operator.
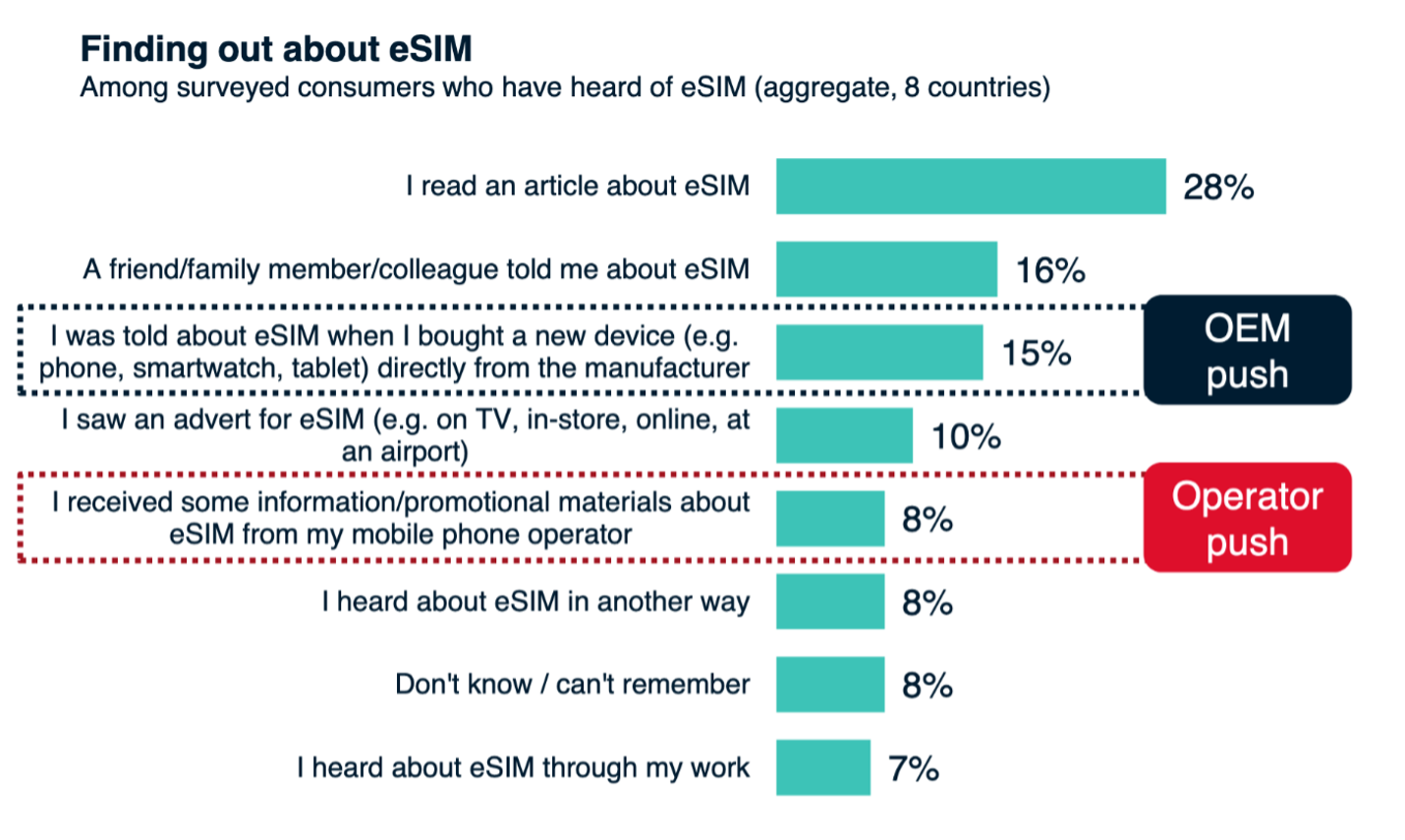 Source: GSMA Intelligence
Source: GSMA Intelligence
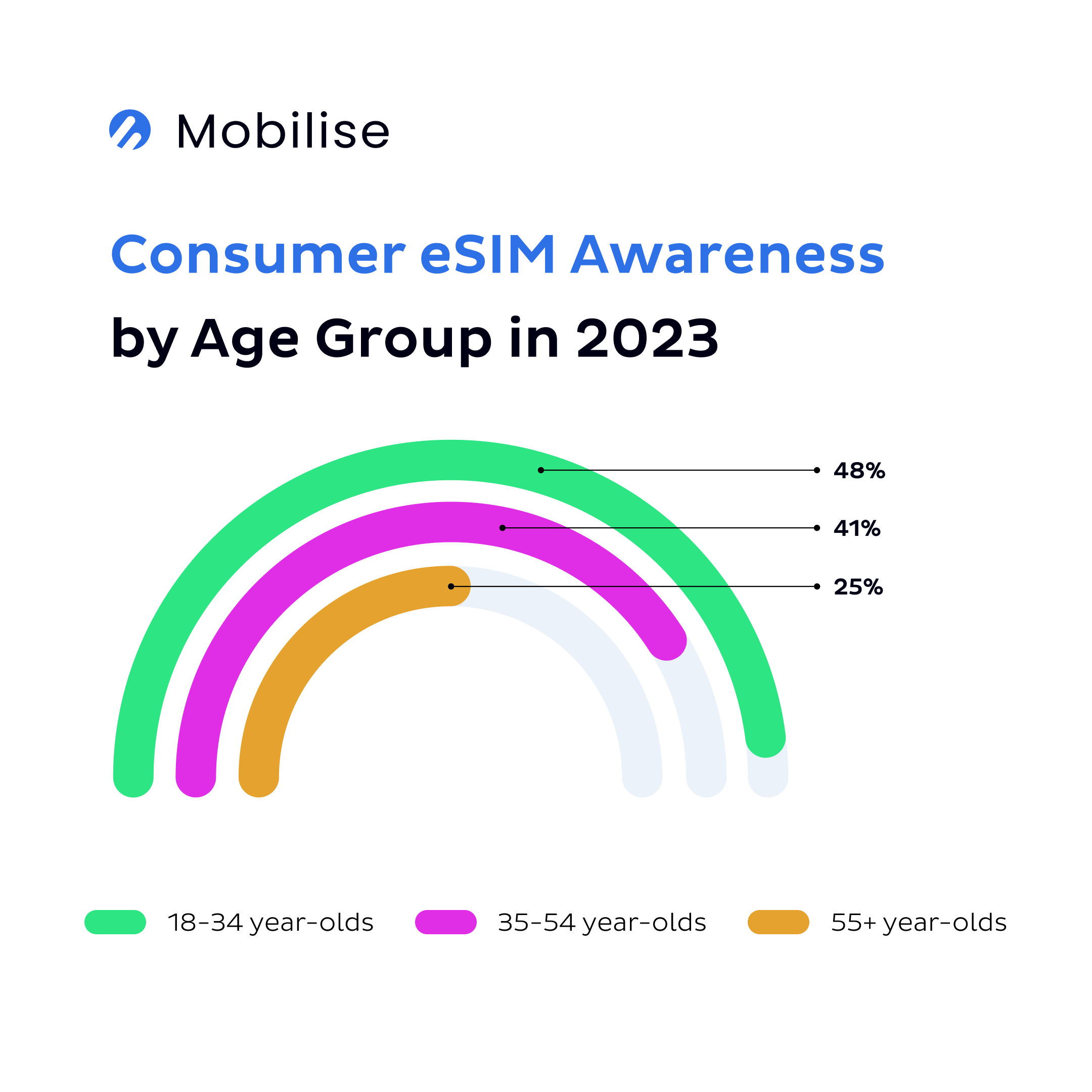
According to a GSMA Intelligence report, eSIM awareness among consumers was around 20% in 2020. More recent data suggests that 2023 awareness was still lower than 30%. The level varies across different regions, generations, and smartphone brands owned by consumers. But that doesn’t change the fact that the awareness is low and growing slowly.
So, are consumers unwilling to try new technology? It’s quite the opposite of what the eSIM statistics suggest.
According to a recent eSIM Consumer Pulse 2022 report, 81% of 2,500 surveyed customers across the US, UK, and Australia were in favour of or open to eSIM-only smartphones. Additionally, only 15% of consumers don’t want their provider to sell eSIMs, compared to 58% who do.
This perfectly highlights the gap in efforts to improve the uptake for the eSIM future.
Regulatory Hurdles
It’s not just traditional players and consumers that affect eSIM adoption. There are plenty of eSIM challenges that also affect adoption.
And one of them is regulatory challenges. Inconsistent standards and certification processes across different regions create obstacles to eSIM deployment. It is crucial to establish clear and consistent regulatory frameworks to ensure interoperability.
The GSMA has developed a compliance framework for eSIM-capable devices, eUICCs, and Subscription Management servers, as shown in the image below. These requirements prioritise eSIM security assurance, functionality, and interoperability. Such frameworks will promote compatibility, making it easier for users to switch between different mobile network operators and devices without hassle.
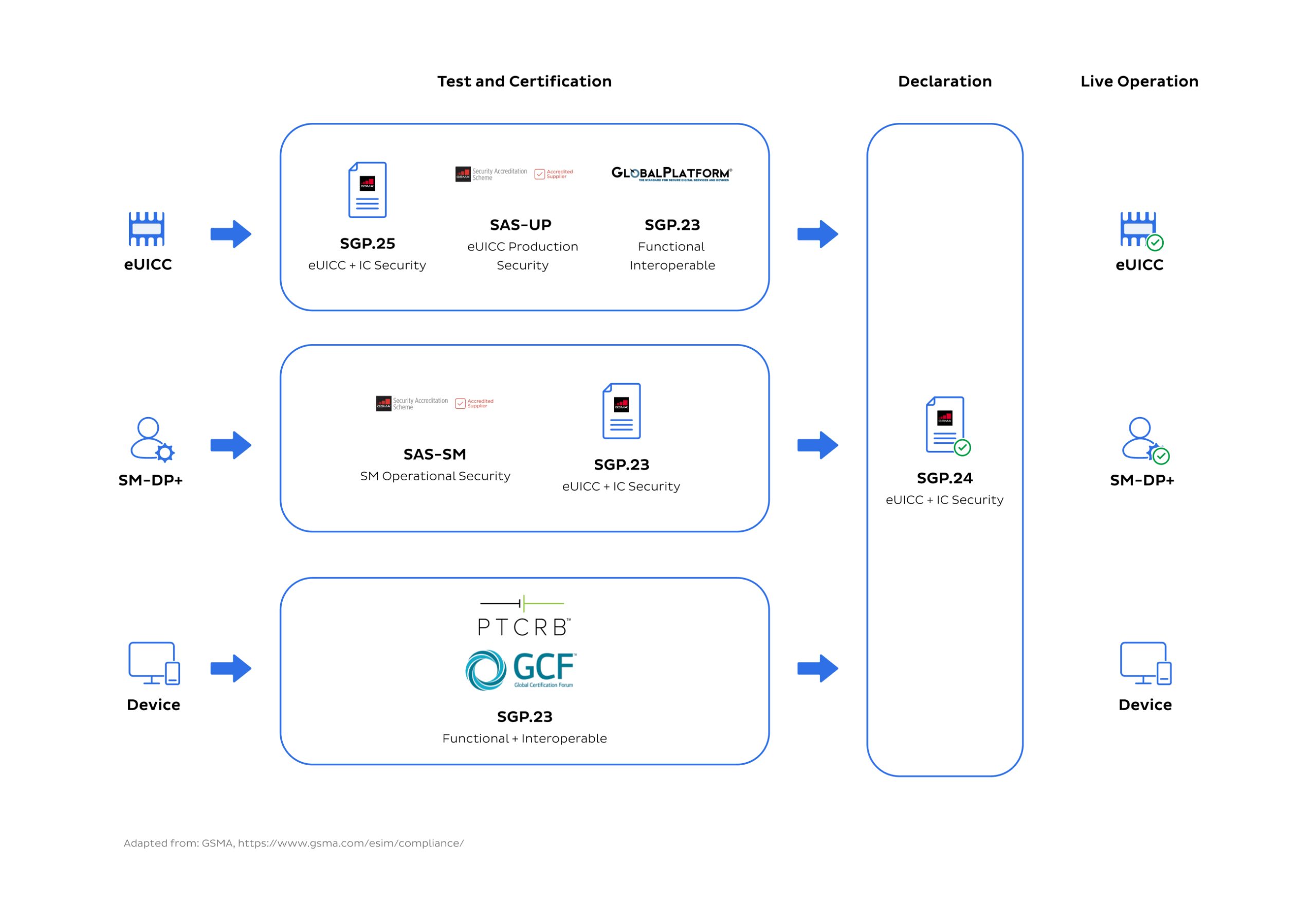
While this is a robust compliance framework for new players in the eSIM game, it may seem daunting about where to even start ensuring that their service can be compliant.
Telecom SaaS providers are crucial in promoting eSIM adoption by influencing policymakers and advocating regulatory reforms. By engaging with policymakers, they can highlight the benefits of eSIM technology and the need for supportive regulatory frameworks. Through advocacy efforts, they can create awareness and promote the adoption of eSIM technology, which will enable users to experience the technology’s benefits, such as flexibility, cost savings, and improved user experience.
Cost Considerations
The initial investment and ongoing costs associated with implementing eSIM technology present a business adoption barrier. However, potential long-term cost savings through reduced SIM card distribution and management expenses are significant.

Businesses encounter initial investment and ongoing costs when implementing eSIM technology. However, potential long-term cost savings through reduced SIM card distribution and management expenses make eSIM adoption enticing.
Complexity in Implementation
Technical challenges, such as system integration and compatibility issues, complicate the implementation of eSIM technology. Managing eSIM profiles and provisioning across different devices and platforms adds to this complexity. eSIM vendors offer solutions to simplify implementation processes, including APIs and cloud-based solutions.
Security and Privacy Concerns
There are often security and privacy concerns surrounding eSIM, including the risks of hacking and data breaches, which deter adoption.
Like any technology, eSIMs also have certain risks and vulnerabilities. Some of the potential risks include the possibility of malicious actors intercepting and manipulating eSIM communications, exploiting vulnerabilities in eSIM software or hardware and gaining unauthorised access to sensitive user data stored on the eSIM chip. Additionally, eSIMs can be subject to social engineering attacks or other forms of user error, such as inadvertently exposing login credentials or failing to update software regularly.
However, eSIM offers several advantages over physical SIM security, such as better protection against physical theft or loss, as well as the ability to remotely manage and update eSIM profiles.
eSIM providers must implement encryption and secure provisioning protocols to address these concerns. Providers are advised to adhere to data protection regulations when deploying eSIM technology.
RECOMMENDED READING
Our solution – eSIM as a Service
We have the perfect solution, making implementing eSIM as part of your service offering easier than ever.
Larger service providers already possess the necessary resources, technology, relationships, and negotiating power to address consumer eSIM challenges effectively.
Our eSIM as a Service solution empowers Service Providers to create fully digital customer journeys and future-proof their brands. Leveraging our HERO platform’s capabilities and our telecom industry expertise, we enable SPs to swiftly and efficiently launch a successful consumer eSIM offering without the need for complex integrations.

Conclusion
eSIM could change the way we connect. So why is eSIM not popular? It seems there are still a few hurdles to overcome before becoming the standard, including regulation, a lack of support from traditional players in the telco industry and a lack of consumer awareness.
To overcome these challenges, businesses and industry leaders need to work together. By addressing these key challenges and leveraging the opportunities presented, and with the right efforts, eSIM could revolutionise the future of connectivity and become the standard connectivity method.